Detection and identification of old world Leishmania by high resolution melt analysis
- PMID: 20069036
- PMCID: PMC2797090
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000581
Detection and identification of old world Leishmania by high resolution melt analysis
Abstract
Background: Three major forms of human disease, cutaneous leishmaniasis, visceral leishmaniasis and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, are caused by several leishmanial species whose geographic distribution frequently overlaps. These Leishmania species have diverse reservoir hosts, sand fly vectors and transmission patterns. In the Old World, the main parasite species responsible for leishmaniasis are Leishmania infantum, L. donovani, L. tropica, L. aethiopica and L. major. Accurate, rapid and sensitive diagnostic and identification procedures are crucial for the detection of infection and characterization of the causative leishmanial species, in order to provide accurate treatment, precise prognosis and appropriate public health control measures.
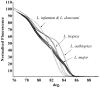
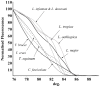
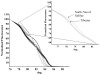
Methods/principal findings: High resolution melt analysis of a real time PCR product from the Internal Transcribed Spacer-1 rRNA region was used to identify and quantify Old World Leishmania in 300 samples from human patients, reservoir hosts and sand flies. Different characteristic high resolution melt analysis patterns were exhibited by L. major, L. tropica, L. aethiopica, and L. infantum. Genotyping by high resolution melt analysis was verified by DNA sequencing or restriction fragment length polymorphism. This new assay was able to detect as little as 2-4 ITS1 gene copies in a 5 microl DNA sample, i.e., less than a single parasite per reaction.
Conclusions/significance: This new technique is useful for rapid diagnosis of leishmaniasis and simultaneous identification and quantification of the infecting Leishmania species. It can be used for diagnostic purposes directly from clinical samples, as well as epidemiological studies, reservoir host investigations and vector surveys.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Schönian G, Mauricio I, Gramiccia M, Cañavate C, Boelaert M, et al. Leishmaniases in the Mediterranean in the era of molecular epidemiology. Trends Parasitol. 2008;24:135–142. - PubMed
-
- Bañuls AL, Guerrini F, Le Pont F, Barrera C, Espinel I, et al. Evidence for hybridization by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and random amplified polymorphic DNA between Leishmania braziliensis and Leishmania panamensis/guyanensis in Ecuador. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1997;44:408–4011. - PubMed
-
- Mauricio IL, Stothard JR, Miles MA. Leishmania donovani complex: genotyping with the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and the mini-exon. Parasitology. 2004;28:263–267. - PubMed
-
- Rioux JA, Lanotte G, Serres E, Pratlong E, Bastien P, et al. Taxonomy of Leishmania. Use of isoenzymes. Suggestions for a new classification. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1990;65:111–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

