The Impact of Adenosine Fast Induction of Myocardial Arrest during CABG on Myocardial Expression of Apoptosis-Regulating Genes Bax and Bcl-2
- PMID: 20069048
- PMCID: PMC2801008
- DOI: 10.4061/2009/658965
The Impact of Adenosine Fast Induction of Myocardial Arrest during CABG on Myocardial Expression of Apoptosis-Regulating Genes Bax and Bcl-2
Abstract
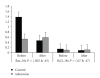
Background. We studied the effect of fast induction of cardiac arrest with denosine on myocardial bax and bcl-2 expression. Methods and Results. 40 elective CABG patients were allocated into two groups. The adenosine group (n = 20) received 250 mug/kg adenosine into the aortic root followed by blood potassium cardioplegia. The control group received potassium cardioplegia in blood. Bcl-2 and bax were measured. Bax was reduced in the postoperative biopsies (1.38 versus 0.47, P = .002) in the control group. Bcl-2 showed a reducing tendency (0.14 versus 0.085, P = .07). After the adenosine treatment, the expression of both bax (0.52 versus 0.59, P = .4) and bcl-2 (0.104 versus 0.107, P = .4) remained unaltered after the operation. Conclusion. Open heart surgery is associated with rapid reduction in the expression of apoptosis regulating genes bax and bcl-2. Fast Adenosine induction abolished changes in their expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiomyocyte apoptosis after antegrade and retrograde cardioplegia during aortic valve surgery.Ann Thorac Surg. 2011 Oct;92(4):1351-7. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.05.065. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011. PMID: 21958782 Clinical Trial.
-
The myocardial protective effect of adenosine as an adjunct to intermittent blood cardioplegia during open heart surgery.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009 Dec;36(6):1018-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.06.033. Epub 2009 Aug 15. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009. PMID: 19683936 Clinical Trial.
-
Improved profile of bad phosphorylation and caspase 3 activation after blood versus crystalloid cardioplegia.Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 Apr;77(4):1384-9; discussion 1389-90. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2003.09.053. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15063271
-
Adenosine attenuates reperfusion-induced apoptotic cell death by modulating expression of Bcl-2 and Bax proteins.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001 Jan;33(1):57-68. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.2000.1275. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001. PMID: 11133223
-
Effect of Fast Cardioplegic Arrest Induced by Adenosine on Cardiac Troponin Levels After Heart Valve Surgery.Heart Lung Circ. 2019 Nov;28(11):1714-1719. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2018.08.017. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Heart Lung Circ. 2019. PMID: 30253969
Cited by
-
The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications of PANoptosis in ischemic diseases.Apoptosis. 2025 Sep 7. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02157-2. Online ahead of print. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40914912 Review.
References
-
- Cooper WA, Duarte IG, Thourani VH, et al. Hypothermic circulatory arrest causes multisystem vascular endothelial dysfunction and apoptosis. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 2000;69(3):696–703. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt JP, Schrader J, Schunkert H, Birnbaum DE, Aebert H. Role of apoptosis in myocardial stunning after open heart surgery. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 2002;73(4):1229–1235. - PubMed
-
- Yeh C-H, Wang Y-C, Wu Y-C, Chu J-J, Lin PJ. Continuous tepid blood cardioplegia can preserve coronary endothelium and ameliorate the occurrence of cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Chest. 2003;123(5):1647–1654. - PubMed
-
- Fischer UM, Cox CS, Jr., Laine GA, Mehlhorn U, Bloch W, Allen SJ. Induction of cardioplegic arrest immediately activates the myocardial apoptosis signal pathway. American Journal of Physiology. 2007;292(3):H1630–H1633. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z-K, Laurikka J, Saraste A, et al. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis and ischemic preconditioning in open heart operations. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 2003;76(2):528–534. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
