Correctness of protein identifications of Bacillus subtilis proteome with the indication on potential false positive peptides supported by predictions of their retention times
- PMID: 20069061
- PMCID: PMC2801521
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/718142
Correctness of protein identifications of Bacillus subtilis proteome with the indication on potential false positive peptides supported by predictions of their retention times
Abstract
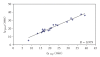
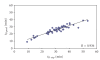
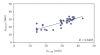
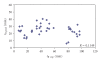
The predictive capability of the retention time prediction model based on quantitative structure-retention relationships (QSRR) was tested. QSRR model was derived with the use of set of peptides identified with the highest scores and originated from 8 known proteins annotated as model ones. The predictive ability of the QSRR model was verified with the use of a Bacillus subtilis proteome digest after separation and identification of the peptides by LC-ESI-MS/MS. That ability was tested with three sets of testing peptides assigned to the proteins identified with different levels of confidence. First, the set of peptides identified with the highest scores achieved in the search were considered. Hence, proteins identified on the basis of more than one peptide were taken into account. Furthermore, proteins identified on the basis of just one peptide were also considered and, depending on the possessed scores, both above and below the assumed threshold, were analyzed in two separated sets. The QSRR approach was applied as the additional constraint in proteomic research verifying results of MS/MS ion search and confirming the correctness of the peptides identifications along with the indication of the potential false positives.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteomic analysis of small acid soluble proteins in the spore core of Bacillus subtilis ΔprpE and 168 strains with predictions of peptides liquid chromatography retention times as an additional tool in protein identification.Proteome Sci. 2010 Nov 22;8:60. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-8-60. Proteome Sci. 2010. PMID: 21092197 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting non-linear relationships between retention time and molecular structure of peptides originating from proteomes and comparing three multivariate approaches.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Aug 5;127:94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.01.055. Epub 2016 Jan 27. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016. PMID: 26856456
-
Comprehensive absolute quantification of the cytosolic proteome of Bacillus subtilis by data independent, parallel fragmentation in liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS(E)).Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Apr;13(4):1008-19. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.032631. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24696501 Free PMC article.
-
Predictions of peptides' retention times in reversed-phase liquid chromatography as a new supportive tool to improve protein identification in proteomics.Proteomics. 2009 Feb;9(4):835-47. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800544. Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19160394 Review.
-
Proteomic analyses using an accurate mass and time tag strategy.Biotechniques. 2004 Oct;37(4):621-4, 626-33, 636 passim. doi: 10.2144/04374RV01. Biotechniques. 2004. PMID: 15517975 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis of small acid soluble proteins in the spore core of Bacillus subtilis ΔprpE and 168 strains with predictions of peptides liquid chromatography retention times as an additional tool in protein identification.Proteome Sci. 2010 Nov 22;8:60. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-8-60. Proteome Sci. 2010. PMID: 21092197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fröhlich T, Arnold GJ. Proteome research based on modern liquid chromatography—tandem mass spectrometry: separation, identification and quantification. Journal of Neural Transmission. 2006;113(8):973–994. - PubMed
-
- Shinoda K, Sugimoto M, Tomita M, Ishihama Y. Informatics for peptide retention properties in proteomic LC-MS. Proteomics. 2008;8(4):787–798. - PubMed
-
- Yates JR, III, Eng JK, McCormack AL, Schieltz D. Method to correlate tandem mass spectra of modified peptides to amino acid sequences in the protein database. Analytical Chemistry. 1995;67(8):1426–1436. - PubMed
-
- Anderson DC, Li W, Payan DG, Noble WS. A new algorithm for the evaluation of shotgun peptide sequencing in proteomics: support vector machine classification of peptide MS/MS spectra and SEQUEST scores. Journal of Proteome Research. 2003;2(2):137–146. - PubMed
-
- Eng JK, McCormack AL, Yates JR., III An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry. 1994;5(11):976–989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

