Small-animal SPECT and SPECT/CT: application in cardiovascular research
- PMID: 20069298
- PMCID: PMC2918793
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-009-1321-8
Small-animal SPECT and SPECT/CT: application in cardiovascular research
Abstract
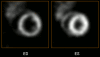
Preclinical cardiovascular research using noninvasive radionuclide and hybrid imaging systems has been extensively developed in recent years. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is based on the molecular tracer principle and is an established tool in noninvasive imaging. SPECT uses gamma cameras and collimators to form projection data that are used to estimate (dynamic) 3-D tracer distributions in vivo. Recent developments in multipinhole collimation and advanced image reconstruction have led to sub-millimetre and sub-half-millimetre resolution SPECT in rats and mice, respectively. In this article we review applications of microSPECT in cardiovascular research in which information about the function and pathology of the myocardium, vessels and neurons is obtained. We give examples on how diagnostic tracers, new therapeutic interventions, pre- and postcardiovascular event prognosis, and functional and pathophysiological heart conditions can be explored by microSPECT, using small-animal models of cardiovascular disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small-animal SPECT and SPECT/CT: important tools for preclinical investigation.J Nucl Med. 2008 Oct;49(10):1651-63. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.055442. Epub 2008 Sep 15. J Nucl Med. 2008. PMID: 18794275 Review.
-
Dynamic SPECT measurement of absolute myocardial blood flow in a porcine model.J Nucl Med. 2014 Oct;55(10):1685-91. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.139782. Epub 2014 Sep 4. J Nucl Med. 2014. PMID: 25189340
-
Recent advances in SPECT imaging.J Nucl Med. 2007 Apr;48(4):661-73. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.106.032680. J Nucl Med. 2007. PMID: 17401106
-
New cardiac cameras: single-photon emission CT and PET.Semin Nucl Med. 2014 Jul;44(4):232-51. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2014.04.003. Semin Nucl Med. 2014. PMID: 24948149 Review.
-
Prognostic evaluation in obese patients using a dedicated multipinhole cadmium-zinc telluride SPECT camera.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Feb;32(2):355-361. doi: 10.1007/s10554-015-0770-3. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26424491
Cited by
-
Serial examination of cardiac function and perfusion in growing rats using SPECT/CT for small animals.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 13;10(1):160. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57032-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31932657 Free PMC article.
-
Performance assessment of the single photon emission microscope: high spatial resolution SPECT imaging of small animal organs.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013 Nov;46(11):936-942. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20132764. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013. PMID: 24270908 Free PMC article.
-
The frontier of live tissue imaging across space and time.Cell Stem Cell. 2021 Apr 1;28(4):603-622. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.02.010. Cell Stem Cell. 2021. PMID: 33798422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptation, Commissioning, and Evaluation of a 3D Treatment Planning System for High-Resolution Small-Animal Irradiation.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jun;15(3):460-71. doi: 10.1177/1533034615584522. Epub 2015 May 6. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 25948321 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Myocardial Perfusion Defect Size in Rats: Comparison between Quantitative Perfusion SPECT and Autoradiography.Mol Imaging Biol. 2018 Aug;20(4):544-550. doi: 10.1007/s11307-018-1159-1. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018. PMID: 29340889
References
-
- Recchia FA, Lionetti V. Animal models of dilated cardiomyopathy for translational research. Vet Res Commun. 2007;31(Suppl 1):35–41. - PubMed
-
- Moon A. Mouse models of congenital cardiovascular disease. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008;84:171–248. - PubMed
-
- Franc BL, Acton PD, Mari C, Hasegawa BH. Small-animal SPECT and SPECT/CT: important tools for preclinical investigation. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(10):1651–1663. - PubMed
-
- Jaszczak RJ, Li JY, Wang HL, Zalutsky MR, Coleman RE. Pinhole collimation for ultra-high-resolution, small-field-of-view SPECT. Phys Med Biol. 1994;39:425–437. - PubMed
-
- Ishizu K, Mukai T, Yonekura Y, et al. Ultra-high-resolution SPECT system using four pinhole collimators for small animal studies. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:2282–2287. - PubMed

