Use of flow cytometric methods to quantify protein-protein interactions
- PMID: 20069525
- PMCID: PMC2849137
- DOI: 10.1002/0471142956.cy1311s51
Use of flow cytometric methods to quantify protein-protein interactions
Abstract
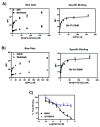
A method is described for the quantitative analysis of protein-protein interactions using the flow cytometry protein interaction assay (FCPIA). This method is based upon immobilizing protein on a polystyrene bead, incubating these beads with a fluorescently labeled binding partner, and assessing the sample for bead-associated fluorescence in a flow cytometer. This method can be used to calculate protein-protein interaction affinities or to perform competition experiments with unlabeled binding partners or small molecules. Examples described in this protocol highlight the use of this assay in the quantification of the affinity of binding partners of the regulator of G-protein signaling protein, RGS19, in either a saturation or a competition format. An adaptation of this method that is compatible for high-throughput screening is also provided.
Figures



References
-
- Sarvazyan NA, Remmers AE, Neubig RR. Determinants of gi1alpha and beta gamma binding. Measuring high affinity interactions in a lipid environment using flow cytometry. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(14):7934–40. - PubMed
-
- Simons PC, et al. Ligand-receptor-G-protein molecular assemblies on beads for mechanistic studies and screening by flow cytometry. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64(5):1227–38. - PubMed
-
- Sklar LA, et al. Flow cytometric analysis of ligand-receptor interactions and molecular assemblies. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2002;31:97–119. - PubMed
-
- Roman DL, et al. Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of RGS4 using a high-throughput flow cytometry protein interaction assay. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;71(1):169–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

