Stem cell side population analysis and sorting using DyeCycle violet
- PMID: 20069528
- PMCID: PMC7375400
- DOI: 10.1002/0471142956.cy0930s51
Stem cell side population analysis and sorting using DyeCycle violet
Abstract
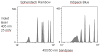
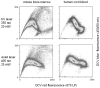
Hoechst side population (SP) analysis has proven to be a valuable technique for identifying and sorting stem and early progenitor cells in a variety of tissues and species. In this method, the DNA binding dye Hoechst 33342 is loaded into the cell population of interest; stem cells preferentially exclude this dye, and these low-fluorescence cells can be detected by flow cytometry. However, Hoechst SP analysis usually requires a flow cytometer equipped with an ultraviolet laser source for optimal performance. Unfortunately, ultraviolet lasers are expensive and are not common fixtures on flow cytometers. Violet laser diodes emitting in the 395- to 410-nm range are less expensive and have become much more common on flow cytometers, but do not provide optimal excitation of Hoechst 33342. DyeCycle Violet is a cell-permeable DNA binding dye with a chemical structure similar to Hoechst 33342, but with a longer excitation maximum. DyeCycle Violet can be substituted for Hoechst 33342 when performing side population analysis on a cytometer with a violet laser source. The procedure for DyeCycle Violet labeling for side population is described, as well as the limitations particular to this dye.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Side population analysis using a violet-excited cell-permeable DNA binding dye.Stem Cells. 2007 Apr;25(4):1029-36. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0567. Epub 2006 Dec 21. Stem Cells. 2007. PMID: 17185610
-
The minimal instrumentation requirements for Hoechst side population analysis: stem cell analysis on low-cost flow cytometry platforms.Stem Cells. 2006 Nov;24(11):2573-81. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0266. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Stem Cells. 2006. PMID: 16888279
-
Discrimination of the Hoechst side population in mouse bone marrow with violet and near-ultraviolet laser diodes.Cytometry A. 2004 Jan;57(1):45-52. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.10109. Cytometry A. 2004. PMID: 14699605
-
Flow cytometry of the side population (SP).Curr Protoc Cytom. 2013;Chapter 9:9.23.1-9.23.20. doi: 10.1002/0471142956.cy0923s64. Curr Protoc Cytom. 2013. PMID: 23546779 Review.
-
A side order of stem cells: the SP phenotype.Stem Cells. 2006 Jan;24(1):3-12. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2005-0116. Stem Cells. 2006. PMID: 16449630 Review.
Cited by
-
β-catenin/Tcf-signaling appears to establish the murine ovarian surface epithelium (OSE) and remains active in selected postnatal OSE cells.BMC Dev Biol. 2012 Jun 8;12:17. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-12-17. BMC Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22682531 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of multidrug resistant human tissues by overexpression of the ABCG2 multidrug transporter in embryonic stem cells.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 12;13(4):e0194925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194925. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29649238 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Gastric Cancer Stem Cells: A Meta-Analysis of the Current Status.J Clin Med. 2019 May 9;8(5):639. doi: 10.3390/jcm8050639. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31075910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and applications of prostate side population cells based on dye cycle violet efflux.Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2011 Feb;Chapter 22:Unit 22.2. doi: 10.1002/0471140856.tx2202s47. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21400686 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin inhibits stem cell proliferation in human leiomyoma via TGF-β3 and Wnt/β-Catenin pathways.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Mar;26(5):1684-1698. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17211. Epub 2022 Feb 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35118811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Challen GA, Little MH. A side order of stem cells: The SP phenotype. Stem Cells. 2006;24:3–12. Comprehensive review of Hoechst SP analysis. - PubMed
-
- Goodell MA. Current Protocols in Cytometry. John Wiley and Sons; NY, NY: 2005. Stem cell identification and sorting using the Hoechst 33342 side population (SP) pp. 9.18.1–9.18.11. Detailed Hoechst SP method. - PubMed
-
- Hadnagy A, Gaboury L, Beaulieu R, Balicki D. SP analysis may be used to identify cancer stem cell populations. Experimental Cell Research. 2006;312:3701–3710. A review of Hoechst SP analysis in cancer stem cells. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

