Galaxy: a web-based genome analysis tool for experimentalists
- PMID: 20069535
- PMCID: PMC4264107
- DOI: 10.1002/0471142727.mb1910s89
Galaxy: a web-based genome analysis tool for experimentalists
Abstract
High-throughput data production has revolutionized molecular biology. However, massive increases in data generation capacity require analysis approaches that are more sophisticated, and often very computationally intensive. Thus, making sense of high-throughput data requires informatics support. Galaxy (http://galaxyproject.org) is a software system that provides this support through a framework that gives experimentalists simple interfaces to powerful tools, while automatically managing the computational details. Galaxy is distributed both as a publicly available Web service, which provides tools for the analysis of genomic, comparative genomic, and functional genomic data, or a downloadable package that can be deployed in individual laboratories. Either way, it allows experimentalists without informatics or programming expertise to perform complex large-scale analysis with just a Web browser.
Figures
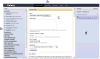



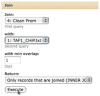


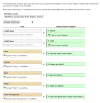


References
-
- Karolchik D, Kuhn RM, Baertsch R, Barber GP, Clawson H, Diekhans M, Giardine B, Harte RA, Hinrichs AS, Hsu F, Miller W, Pedersen JS, Pohl A, Raney BJ, Rhead B, Rosenbloom KR, Smith KE, Stanke M, Thakkapallayil A, Trumbower H, Wang T, Zweig AS, Haussler D, Kent WJ. The UCSC Genome Browser Database: 2008 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36:D773–9. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

