An active dimanganese(III)-tyrosyl radical cofactor in Escherichia coli class Ib ribonucleotide reductase
- PMID: 20070127
- PMCID: PMC3190568
- DOI: 10.1021/bi902106n
An active dimanganese(III)-tyrosyl radical cofactor in Escherichia coli class Ib ribonucleotide reductase
Abstract
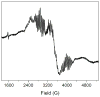
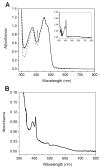
Escherichia coli class Ib ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) converts nucleoside 5'-diphosphates to deoxynucleoside 5'-diphosphates and is expressed under iron-limited and oxidative stress conditions. This RNR is composed of two homodimeric subunits: alpha2 (NrdE), where nucleotide reduction occurs, and beta2 (NrdF), which contains an unidentified metallocofactor that initiates nucleotide reduction. nrdE and nrdF are found in an operon with nrdI, which encodes an unusual flavodoxin proposed to be involved in metallocofactor biosynthesis and/or maintenance. Ni affinity chromatography of a mixture of E. coli (His)(6)-NrdI and NrdF demonstrated tight association between these proteins. To explore the function of NrdI and identify the metallocofactor, apoNrdF was loaded with Mn(II) and incubated with fully reduced NrdI (NrdI(hq)) and O(2). Active RNR was rapidly produced with 0.25 +/- 0.03 tyrosyl radical (Y*) per beta2 and a specific activity of 600 units/mg. EPR and biochemical studies of the reconstituted cofactor suggest it is Mn(III)(2)-Y*, which we propose is generated by Mn(II)(2)-NrdF reacting with two equivalents of HO(2)(-), produced by reduction of O(2) by NrdF-bound NrdI(hq). In the absence of NrdI(hq), with a variety of oxidants, no active RNR was generated. By contrast, a similar experiment with apoNrdF loaded with Fe(II) and incubated with O(2) in the presence or absence of NrdI(hq) gave 0.2 and 0.7 Y*/beta2 with specific activities of 80 and 300 units/mg, respectively. Thus NrdI(hq) hinders Fe(III)(2)-Y* cofactor assembly in vitro. We propose that NrdI is an essential player in E. coli class Ib RNR cluster assembly and that the Mn(III)(2)-Y* cofactor, not the diferric-Y* one, is the active metallocofactor in vivo.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bacillus subtilis class Ib ribonucleotide reductase is a dimanganese(III)-tyrosyl radical enzyme.Biochemistry. 2011 Jun 28;50(25):5615-23. doi: 10.1021/bi200348q. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21561096 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli class Ib ribonucleotide reductase contains a dimanganese(III)-tyrosyl radical cofactor in vivo.Biochemistry. 2011 Mar 15;50(10):1672-81. doi: 10.1021/bi101881d. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21250660 Free PMC article.
-
NrdI, a flavodoxin involved in maintenance of the diferric-tyrosyl radical cofactor in Escherichia coli class Ib ribonucleotide reductase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 23;105(38):14383-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807348105. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18799738 Free PMC article.
-
Formation and function of the Manganese(IV)/Iron(III) cofactor in Chlamydia trachomatis ribonucleotide reductase.Biochemistry. 2008 Dec 30;47(52):13736-44. doi: 10.1021/bi8017625. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 19061340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of metallation and active cofactor assembly in the class Ia and Ib ribonucleotide reductases: diiron or dimanganese?Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011 Apr;15(2):284-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.12.001. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21216656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid X-ray photoreduction of dimetal-oxygen cofactors in ribonucleotide reductase.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 5;288(14):9648-9661. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.438796. Epub 2013 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23400774 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the initiation of free radical formation in the Class Ib ribonucleotide reductases in Mycobacteria.Curr Res Struct Biol. 2024 Sep 18;8:100157. doi: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2024.100157. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 39399574 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic studies of the iron and manganese reconstituted tyrosyl radical in Bacillus cereus ribonucleotide reductase R2 protein.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033436. Epub 2012 Mar 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22432022 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for assembly of the Mn(IV)/Fe(III) cofactor in the class Ic ribonucleotide reductase from Chlamydia trachomatis.Biochemistry. 2013 Sep 17;52(37):6424-36. doi: 10.1021/bi400819x. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23924396 Free PMC article.
-
Ether cross-link formation in the R2-like ligand-binding oxidase.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018 Aug;23(6):879-886. doi: 10.1007/s00775-018-1583-3. Epub 2018 Jun 26. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29946980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nordlund P, Reichard P. Ribonucleotide reductases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:681–706. - PubMed
-
- Uppsten M, Farnegardh M, Jordan A, Eliasson R, Eklund H, Uhlin U. Structure of the large subunit of class Ib ribonucleotide reductase from Salmonella typhimurium and its complexes with allosteric effectors. J Mol Biol. 2003;330:87–97. - PubMed
-
- McHugh JP, Rodriguez-Quiñones F, Abdul-Tehrani H, Svistunenko DA, Poole RK, Cooper CE, Andrews SC. Global iron-dependent gene regulation in Escherichia coli A new mechanism for iron homeostasis. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:29478–29486. - PubMed
-
- Vassinova N, Kozyrev D. A method for direct cloning of Fur-regulated genes: identification of seven new Fur-regulated loci in Escherichia coli. Microbiology. 2000;146:3171–3182. - PubMed
-
- Monje-Casas F, Jurado J, Prieto-Alamo MJ, Holmgren A, Pueyo C. Expression analysis of the nrdHIEF operon from Escherichia coli Conditions that trigger the transcript level in vivo . J Biol Chem. 2001;276:18031–18037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

