Irreversible inactivation of glutathione peroxidase 1 and reversible inactivation of peroxiredoxin II by H2O2 in red blood cells
- PMID: 20070187
- PMCID: PMC2875961
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2009.2701
Irreversible inactivation of glutathione peroxidase 1 and reversible inactivation of peroxiredoxin II by H2O2 in red blood cells
Abstract
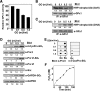
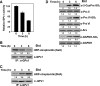
Catalase, glutathione peroxidase1 (GPx1), and peroxiredoxin (Prx) II are the principal enzymes responsible for peroxide elimination in RBC. We have now evaluated the relative roles of these enzymes by studying inactivation of GPx1 and Prx II in human RBCs. Mass spectrometry revealed that treatment of GPx1 with H(2)O(2) converts the selenocysteine residue at its active site to dehydroalanine (DHA). We developed a blot method for detection of DHA-containing proteins, with which we observed that the amount of DHA-containing GPx1 increases with increasing RBC density, which is correlated with increasing RBC age. Given that the conversion of selenocysteine to DHA is irreversible, the content of DHA-GPx1 in each RBC likely reflects total oxidative stress experienced by the cell during its lifetime. Prx II is inactivated by occasional hyperoxidation of its catalytic cysteine to cysteine sulfinic acid during catalysis. We believe that the activity of sulfiredoxin in RBCs is sufficient to counteract the hyperoxidation of Prx II that occurs in the presence of the basal level of H(2)O(2) flux resulting from hemoglobin autoxidation. If the H(2)O(2) flux is increased above the basal level, however, the sulfinic Prx II begins to accumulate. In the presence of an increased H(2)O(2) flux, inhibition of catalase accelerated the accumulation of sulfinic Prx II, indicative of the protective role of catalase.
Figures
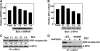




References
-
- Andersen HR. Nielsen JB. Nielsen F. Grandjean P. Antioxidative enzyme activities in human erythrocytes. Clin Chem. 1997;43:562–568. - PubMed
-
- Awasthi YC. Beutler E. Srivastava SK. Purification and properties of human erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1975;250:5144–5149. - PubMed
-
- Bartosz G. Aging of the erythrocyte. VII. On the possible causes of inactivation of red cell enzymes. Mech Ageing Dev. 1980;13:379–385. - PubMed
-
- Beutler E. The hemolytic effect of primaquine and related compounds: A review. Blood. 1959;14:103–139. - PubMed
-
- Biteau B. Labarre J. Toledano MB. ATP-dependent reduction of cysteine-sulphinic acid by S. cerevisiae sulphiredoxin. Nature. 2003;425:980–984. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
