Ecogenomics of respiratory diseases of public health significance
- PMID: 20070197
- PMCID: PMC3402173
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.012809.103633
Ecogenomics of respiratory diseases of public health significance
Abstract
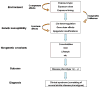
Gene-environment interactions are the indisputable cause of most respiratory diseases. However, we still have very limited understanding of the mechanisms that guide these interactions. Although the conceptual approaches to environmental genomics were established several decades ago, the tools are only now available to better define the mechanisms that underlie the interactions among these important etiological features of lung disease. In this article, we summarize recent insights in the environmental genomics (ecogenomics) of common nonmalignant respiratory diseases (asthma, COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, and respiratory infections), describe the framework of gene-environment interactions that inform the pathogenesis of respiratory diseases, and propose future research directions that will help translate scientific advances into public health gains.
Figures
Comment in
-
Overview of the symposium on public health significance of genomics and eco-genetics.Annu Rev Public Health. 2010;31:1-8. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.012809.103639. Annu Rev Public Health. 2010. PMID: 20001819
References
-
- Adams PF, Hendershot GE, Marano MA. Current estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 1996. Vital Health Stat. 1999;10:1–203. - PubMed
-
- Akolkar PN, Gulwani-Akolkar B, Heresbach D, Lin XY, Fisher S, et al. Differences in risk of Crohn’s disease in offspring of mothers and fathers with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92:2241–44. - PubMed
-
- Anthonisen NR, Skeans MA, Wise RA, Manfreda J, Kanner RE, Connett JE. The effects of a smoking cessation intervention on 14.5-year mortality: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Int Med. 2005;142:233–39. - PubMed
-
- Armanios MY, Chen JJ, Cogan JD, Alder JK, Ingersoll RG, et al. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1317–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

