Distribution and expression of CD200 in the rat respiratory system under normal and endotoxin-induced pathological conditions
- PMID: 20070425
- PMCID: PMC2829398
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01190.x
Distribution and expression of CD200 in the rat respiratory system under normal and endotoxin-induced pathological conditions
Abstract
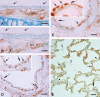
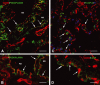
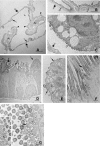
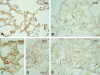
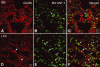
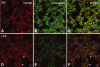
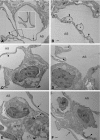
In vivo and in vitro studies have clearly demonstrated that signaling mediated by the interaction of CD200 and its cognate receptor, CD200R, results in an attenuation of inflammatory or autoimmune responses through multiple mechanisms. The present results have shown a differential expression of CD200 in the respiratory tract of intact rats. Along the respiratory passage, CD200 was specifically distributed at the bronchiolar epithelia with intense CD200 immunoreactivity localized at the apical surface of some ciliated epithelial cells; only a limited expression was detected on the Clara cells extending into the alveolar duct. In the alveolar septum, double immunofluorescence showed intense CD200 immunolabeling on the capillary endothelia. A moderate CD200 labeling was observed on the alveolar type II epithelial cells. It was, however, absent in the alveolar type I epithelial cells and the alveolar macrophages. Immunoelectron microscopic study has revealed a specific distribution of CD200 on the luminal front of the thin portion of alveolar endothelia. During endotoxemia, the injured lungs showed a dose- and time-dependent decline of CD200 expression accompanied by a vigorous infiltration of immune cells, some of them expressing ionized calcium binding adapter protein 1 or CD200. Ultrastructural examination further showed that the marked reduction of CD200 expression was mainly attributable to the loss of alveolar endothelial CD200. It is therefore suggested that CD200 expressed by different lung cells may play diverse roles in immune homeostasis of normal lung, in particular, the molecules on alveolar endothelia that may control regular recruitment of immune cells via CD200-CD200R interaction. Additionally, it may contribute to intense infiltration of immune cells following the loss or inefficiency of CD200 under pathological conditions.
Figures
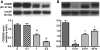
Similar articles
-
CD200 in growing rat lungs: developmental expression and control by dexamethasone.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Mar;359(3):729-42. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2065-8. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25519046
-
Endothelial CD200 is heterogeneously distributed, regulated and involved in immune cell-endothelium interactions.J Anat. 2009 Jan;214(1):183-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.00986.x. J Anat. 2009. PMID: 19166481 Free PMC article.
-
Novel distribution of cluster of differentiation 200 adhesion molecule in glial cells of the peripheral nervous system of rats and its modulation after nerve injury.Neuroscience. 2011 Jun 2;183:32-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.03.049. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21453758
-
CD200-CD200R Pathway in the Regulation of Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Immunotherapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1223:155-165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-35582-1_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32030689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD200/CD200R paired potent inhibitory molecules regulating immune and inflammatory responses; Part I: CD200/CD200R structure, activation, and function.Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2012;55(1):12-7. doi: 10.14712/18059694.2015.68. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2012. PMID: 22696929 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage immunoregulatory pathways in tuberculosis.Semin Immunol. 2014 Dec;26(6):471-85. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25453226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lowering the threshold of lung innate immune cell activation alters susceptibility to secondary bacterial superinfection.J Infect Dis. 2011 Oct 1;204(7):1086-94. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir467. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21881124 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar macrophages: plasticity in a tissue-specific context.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Feb;14(2):81-93. doi: 10.1038/nri3600. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24445666 Review.
-
Secondary bacterial infections in influenza virus infection pathogenesis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2014;385:327-56. doi: 10.1007/82_2014_394. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25027822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble CD200 Correlates With Interleukin-6 Levels in Sera of COPD Patients: Potential Implication of the CD200/CD200R Axis in the Disease Course.Lung. 2017 Feb;195(1):59-68. doi: 10.1007/s00408-016-9962-4. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Lung. 2017. PMID: 27864635
References
-
- Alam T, An MR, Papaconstantinou J. Differential expression of three C/EBP isoforms in multiple tissues during the acute phase response. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:5021–5024. - PubMed
-
- Aoki T, Matsumoto Y, Hirata K, et al. Expression profiling of genes related to asthma exacerbations. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39:213–221. - PubMed
-
- Barclay AN, Clark MJ, McCaughan GW. Neuronal/lymphoid membrane glycoprotein MRC OX-2 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with a light-chain-like structure. Biochem Soc Symp. 1986;51:149–157. - PubMed
-
- Bartling B, Hofmann HS, Weigle B, et al. Down-regulation of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) supports non-small cell lung carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:293–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

