Structural and functional characterization of a novel homodimeric three-finger neurotoxin from the venom of Ophiophagus hannah (king cobra)
- PMID: 20071329
- PMCID: PMC2832981
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.074161
Structural and functional characterization of a novel homodimeric three-finger neurotoxin from the venom of Ophiophagus hannah (king cobra)
Abstract
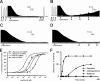
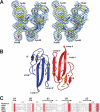
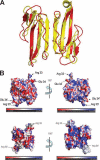
Snake venoms are a mixture of pharmacologically active proteins and polypeptides that have led to the development of molecular probes and therapeutic agents. Here, we describe the structural and functional characterization of a novel neurotoxin, haditoxin, from the venom of Ophiophagus hannah (King cobra). Haditoxin exhibited novel pharmacology with antagonism toward muscle (alphabetagammadelta) and neuronal (alpha(7), alpha(3)beta(2), and alpha(4)beta(2)) nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) with highest affinity for alpha(7)-nAChRs. The high resolution (1.5 A) crystal structure revealed haditoxin to be a homodimer, like kappa-neurotoxins, which target neuronal alpha(3)beta(2)- and alpha(4)beta(2)-nAChRs. Interestingly however, the monomeric subunits of haditoxin were composed of a three-finger protein fold typical of curaremimetic short-chain alpha-neurotoxins. Biochemical studies confirmed that it existed as a non-covalent dimer species in solution. Its structural similarity to short-chain alpha-neurotoxins and kappa-neurotoxins notwithstanding, haditoxin exhibited unique blockade of alpha(7)-nAChRs (IC(50) 180 nm), which is recognized by neither short-chain alpha-neurotoxins nor kappa-neurotoxins. This is the first report of a dimeric short-chain alpha-neurotoxin interacting with neuronal alpha(7)-nAChRs as well as the first homodimeric three-finger toxin to interact with muscle nAChRs.
Figures




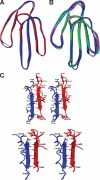
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

