Lrmp/Jaw1 is expressed in sweet, bitter, and umami receptor-expressing cells
- PMID: 20071408
- PMCID: PMC2805811
- DOI: 10.1093/chemse/bjp097
Lrmp/Jaw1 is expressed in sweet, bitter, and umami receptor-expressing cells
Abstract
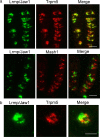
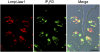
Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-mediated calcium (IP3-Ca2+) signal cascade is an essential process in sweet, bitter, and umami taste signal transduction. Although the main components of this cascade have been identified, the candidate regulators of them in taste tissues are still unclear. In an effort to identify genes involved in taste signal transduction, we found that a gene encoding lymphoid-restricted membrane protein (Lrmp/Jaw1) was expressed in mouse taste tissues. Here we report that Lrmp/Jaw1 is specifically expressed in sweet, bitter, and umami taste receptor-expressing cells of mouse circumvallate, foliate, and fungiform papillae. In addition to this specific expression patterns, we found that Lrmp/Jaw1 is associated with type III IP3 receptor (IP3R3) via its coiled-coil domain in the COS7 heterologous expression system. These results raise the possibility that Lrmp/Jaw1 interacts with IP3R3 in taste cells and suggest an important role for Lrmp/Jaw1 in the IP3-Ca2+ signal cascade in sweet, bitter, and umami taste signal transduction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of gustducin overlaps with that of type III IP3 receptor in taste buds of the rat soft palate.Chem Senses. 2007 Sep;32(7):689-96. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjm036. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Chem Senses. 2007. PMID: 17566068
-
Immunocytochemical evidence for co-expression of Type III IP3 receptor with signaling components of bitter taste transduction.BMC Neurosci. 2001;2:6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-2-6. Epub 2001 Apr 23. BMC Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11346454 Free PMC article.
-
A subset of broadly responsive Type III taste cells contribute to the detection of bitter, sweet and umami stimuli.PLoS Genet. 2020 Aug 13;16(8):e1008925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008925. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32790785 Free PMC article.
-
Bitter-sweet solution in taste transduction.Cell. 2003 Feb 7;112(3):283-4. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00077-1. Cell. 2003. PMID: 12581516 Review.
-
How taste works: cells, receptors and gustatory perception.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2015 Dec;20(5):699-716. doi: 10.1515/cmble-2015-0042. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26447485 Review.
Cited by
-
Making the LINC: SUN and KASH protein interactions.Biol Chem. 2015 Apr;396(4):295-310. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0267. Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25720065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuft cells in the intestine, immunity and beyond.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Dec;21(12):852-868. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-00978-1. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39327439 Review.
-
Regulation of HCN Channels by Protein Interactions.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 20;13:928507. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.928507. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35795651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function of IRAG2 Is Modulated by NO/cGMP in Murine Platelets.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 15;23(12):6695. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126695. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743138 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear forces and cell mechanosensing.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014;126:205-15. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394624-9.00008-7. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014. PMID: 25081619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adler E, Hoon MA, Mueller KL, Chandrashekar J, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS. A novel family of mammalian taste receptors. Cell. 2000;100:693–702. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Mizutani T, Tatsu-ura T, Mikoshiba K. IRBIT, a novel inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptor-binding protein, is released from the IP3 receptor upon IP3 binding to the receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:10602–10612. - PubMed
-
- Behrens TW, Jagadeesh J, Scherle P, Kearns G, Yewdell J, Staudt LM. Jaw1, a lymphoid-restricted membrane protein localized to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Immunol. 1994;153:682–690. - PubMed
-
- Behrens TW, Kearns GM, Rivard JJ, Bernstein HD, Yewdell JW, Staudt LM. Carboxyl-terminal targeting and novel post-translational processing of JAW1, a lymphoid protein of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:23528–23534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

