Mechanisms of immune-mediated liver injury
- PMID: 20071422
- PMCID: PMC2871750
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq009
Mechanisms of immune-mediated liver injury
Abstract
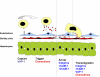
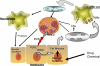
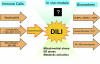
Hepatic inflammation is a common finding during a variety of liver diseases including drug-induced liver toxicity. The inflammatory phenotype can be attributed to the innate immune response generated by Kupffer cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and lymphocytes. The adaptive immune system is also influenced by the innate immune response leading to liver damage. This review summarizes recent advances in specific mechanisms of immune-mediated hepatotoxicity and its application to drug-induced liver injury. Basic mechanisms of activation of lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils and their unique mechanisms of recruitment into the liver vasculature are discussed. In particular, the role of adhesion molecules and various inflammatory mediators in this process are explored. In addition, the authors describe mechanisms of liver cell damage by these inflammatory cells and critically evaluate the functional significance of each cell type for predictive and idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. It is expected that continued advances in our understanding of immune mechanisms of liver injury will lead to an earlier detection of the hepatotoxic potential of drugs under development and to an earlier identification of susceptible individuals at risk for predictive and idiosyncratic drug toxicities.
Figures

References
-
- Adams DH, Eksteen B. Aberrant homing of mucosal T cells and extra-intestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006;6:244–251. - PubMed
-
- Adams DH, Hubscher SG, Fisher NC, Williams A, Robinson M. Expression of E-selectin and E-selectin ligands in human liver inflammation. Hepatology. 1996;24:533–538. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S. Lovastatin-induced lupus erythematosus. Arch. Intern. Med. 1991;151:1667–1668. - PubMed
-
- Andrade RJ, Robles M, Ulzurrun E, Lucena MI. Drug-induced liver injury: insights from genetic studies. Pharmacogenomics. 2009;10:1467–1487. - PubMed
-
- Apte UM, Banerjee A, McRee R, Wellberg E, Ramaiah SK. Role of osteopontin in hepatic neutrophil infiltration during alcoholic steatohepatitis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005;207:25–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

