Impact of Cyclin B2 and Cell division cycle 2 on tubular hyperplasia in progressive chronic renal failure rats
- PMID: 20071461
- PMCID: PMC4380486
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00567.2009
Impact of Cyclin B2 and Cell division cycle 2 on tubular hyperplasia in progressive chronic renal failure rats
Abstract
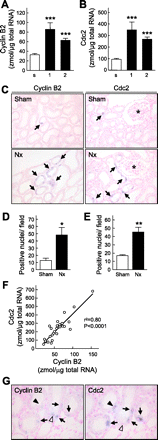
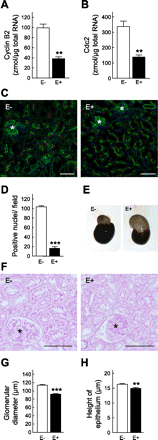
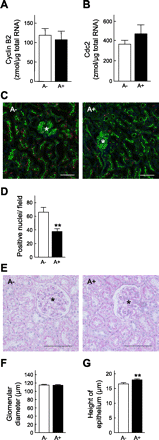
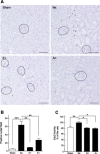
To clarify the specific molecular events of progressive tubular damage in chronic renal failure (CRF), we conducted microarray analyses using isolated proximal tubules from subtotally nephrectomized (Nx) rats as a model of CRF. Our results clearly demonstrated time-dependent changes in gene expression profiles localized to proximal tubules. The expression of mitosis-specific genes Cyclin B2 and Cell division cycle 2 (Cdc2) was significantly and selectively increased in the proximal tubules during the compensated period but decreased to basal level in the end-stage period. Administration of everolimus, a potent inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin, markedly reduced compensatory hypertrophy and hyperplasia of epithelial cells, which was accompanied by complete abolishment of the expression of Cyclin B2 and Cdc2 enhancement; renal function was then severely decreased. Treatment with the Cdc2 inhibitor 2-cyanoethyl alsterpaullone clearly decreased epithelial cell hyperplasia, based on staining of phosphorylated histone H3 and Ki-67, while hypertrophy was not inhibited. In conclusion, we have demonstrated roles of Cyclin B2 and Cdc2 in the epithelial hyperplasia in response to Nx. These results advance the knowledge of the contribution of cell cycle regulators, especially M phase, in pathophysiology of tubular restoration and/or degeneration, and these two molecules are suggested to be a marker for the proliferation of proximal tubular cells in CRF.
Figures


References
-
- Bonventre JV. Dedifferentiation and proliferation of surviving epithelial cells in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 14, Suppl 1: S55–S61, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bottinger EP, Bitzer M. TGF-beta signaling in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 2600–2610, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Chen JK, Chen J, Neilson EG, Harris RC. Role of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in compensatory renal hypertrophy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 1384–1391, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Frazier KS, Paredes A, Dube P, Styer E. Connective tissue growth factor expression in the rat remnant kidney model and association with tubular epithelial cells undergoing transdifferentiation. Vet Pathol 37: 328–335, 2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

