Mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans him-19 show meiotic defects that worsen with age
- PMID: 20071466
- PMCID: PMC2836969
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-09-0811
Mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans him-19 show meiotic defects that worsen with age
Abstract
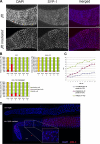
From a screen for meiotic Caenorhabditis elegans mutants based on high incidence of males, we identified a novel gene, him-19, with multiple functions in prophase of meiosis I. Mutant him-19(jf6) animals show a reduction in pairing of homologous chromosomes and subsequent bivalent formation. Consistently, synaptonemal complex formation is spatially restricted and possibly involves nonhomologous chromosomes. Also, foci of the recombination protein RAD-51 occur delayed or cease altogether. Ultimately, mutation of him-19 leads to chromosome missegregation and reduced offspring viability. The observed defects suggest that HIM-19 is important for both homology recognition and formation of meiotic DNA double-strand breaks. It therefore seems to be engaged in an early meiotic event, resembling in this respect the regulator kinase CHK-2. Most astonishingly, him-19(jf6) hermaphrodites display worsening of phenotypes with increasing age, whereas defects are more severe in female than in male meiosis. This finding is consistent with depletion of a him-19-dependent factor during the production of oocytes. Further characterization of him-19 could contribute to our understanding of age-dependent meiotic defects in humans.
Figures


References
-
- Alpi A., Pasierbek P., Gartner A., Loidl J. Genetic and cytological characterization of the recombination protein RAD-51 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosoma. 2003;112:6–16. - PubMed
-
- Colaiacovo M. P., MacQueen A. J., Martinez-Perez E., McDonald K., Adamo A., La Volpe A., Villeneuve A. M. Synaptonemal complex assembly in C. elegans is dispensable for loading strand-exchange proteins but critical for proper completion of recombination. Dev. Cell. 2003;5:463–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

