Single lysophosphatidylcholine components exhibit adjuvant activities in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 20071492
- PMCID: PMC2837973
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00420-09
Single lysophosphatidylcholine components exhibit adjuvant activities in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
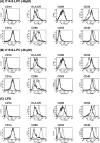
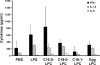
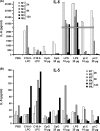
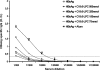
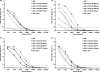
Improving vaccine immunogenicity by developing new adjuvant formulations has long been a goal of vaccinologists. It has previously been shown that a natural mix of lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) from chicken eggs promotes mature dendritic cell (DC) generation in vitro and primes antigen-specific immune responses in mice. In the present study, we dissected the adjuvant potentials of five individual LPC components found in the chicken egg mixture. In vitro analyses of the impact of the individual components on the maturation of human DCs were performed by means of phenotypic analysis, chemokine secretion analysis, and analysis of the ability of mature DC to stimulate T lymphocytes. Two components, C16:0-LPC and C18:0-LPC, were identified to be capable of the upregulation of expression of CD86, HLA-DR, and CD40 on in vitro-cultured monocyte-derived DCs from healthy donors. Both induced the release of chemokines to high concentrations (macrophage inflammatory protein 1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1) or moderate concentrations (interleukin-8 [IL-8], gamma interferon-inducible protein 10). In addition, C16:0-LPC engaged naïve T cells to produce gamma interferon. This suggests that C16:0-LPC and C18:0-LPC have the capacity to promote, at least in vitro, a Th1-oriented response. The intravenous injection of C16:0-LPC or C18:0-LPC into mice resulted in the detectable secretion of IL-6 and IL-5 in sera. Both LPC components were tested for their capacities to act as adjuvants for two selected immunogens: the hepatitis B virus surface antigen and the hepatitis C virus NS3 helicase. The secretion of specific IgG1 was observed with either or both C16:0-LPC and C18:0-LPC, depending on the immunogen tested, and was observed at an efficiency comparable to that of alum. These data identify C16:0-LPC and C18:0-LPC as the active components of the LPC natural mixture. Although discrepancies between the results of the in vitro and in vivo analyses existed, studies with animals suggest that these components can trigger significant and specific humoral-mediated immunity.
Figures
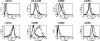

Similar articles
-
Lysophosphatidylcholine is a natural adjuvant that initiates cellular immune responses.Vaccine. 2006 Feb 27;24(9):1254-63. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.09.036. Epub 2005 Sep 30. Vaccine. 2006. PMID: 16229929
-
Cholera toxin promotes the induction of regulatory T cells specific for bystander antigens by modulating dendritic cell activation.J Immunol. 2003 Sep 1;171(5):2384-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.5.2384. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12928385
-
Analysis of anthrax and plague biowarfare vaccine interactions with human monocyte-derived dendritic cells.J Immunol. 2005 Dec 1;175(11):7235-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.11.7235. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16301628
-
Efficient antitumor immunity derived from maturation of dendritic cells that had phagocytosed apoptotic/necrotic tumor cells.Int J Cancer. 2001 Aug 15;93(4):539-48. doi: 10.1002/ijc.1365. Int J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11477558
-
Uncarinic acid C plus IFN-γ generates monocyte-derived dendritic cells and induces a potent Th1 polarization with capacity to migrate.Cell Immunol. 2010;266(1):104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2010.09.004. Epub 2010 Sep 18. Cell Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20933226
Cited by
-
A new passive immune strategy based on IgY antibodies as a key element to control neonatal calf diarrhea in dairy farms.BMC Vet Res. 2020 Jul 29;16(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02476-3. BMC Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32727468 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lysophosphatidylcholine on Jejuna Morphology and Its Potential Mechanism.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jun 20;9:911496. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.911496. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35795789 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment With Lipopolysaccharide Induces Distinct Changes in Metabolite Profile and Body Weight in 129Sv and Bl6 Mouse Strains.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 27;11:371. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00371. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32292347 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Lipid Biomarkers for Chronic Joint Pain Associated with Different Joint Diseases.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 9;13(2):342. doi: 10.3390/biom13020342. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830710 Free PMC article.
-
Egg yolk IgY: protection against rotavirus induced diarrhea and modulatory effect on the systemic and mucosal antibody responses in newborn calves.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2011 Aug 15;142(3-4):156-69. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 May 7. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2011. PMID: 21652087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar, J. C., and E. G. Rodriguez. 2007. Vaccine adjuvants revisited. Vaccine 25:3752-3762. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, H., and J. Gauldie. 1994. The acute phase response. Immunol. Today 15:74-80. - PubMed
-
- Braun, L. J., A. Tyagi, S. Perkins, J. Carpenter, D. Sylvester, M. Guy, D. Kristensen, and D. Chen. 2009. Development of a freeze-stable formulation for vaccines containing aluminum salt adjuvants. Vaccine 27:72-79. - PubMed
-
- Cabana, V. G., J. N. Siegel, and S. M. Sabesin. 1989. Effects of the acute phase response on the concentration and density distribution of plasma lipids and apolipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 30:39-49. - PubMed
-
- Coutant, F., S. Agaugue, L. Perrin-Cocon, P. Andre, and V. Lotteau. 2004. Sensing environmental lipids by dendritic cell modulates its function. J. Immunol. 172:54-60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

