Loss of Cav1.3 channels reveals the critical role of L-type and BK channel coupling in pacemaking mouse adrenal chromaffin cells
- PMID: 20071512
- PMCID: PMC6633011
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4961-09.2010
Loss of Cav1.3 channels reveals the critical role of L-type and BK channel coupling in pacemaking mouse adrenal chromaffin cells
Abstract
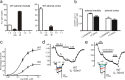
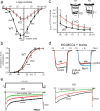
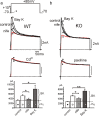
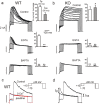
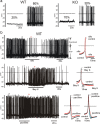
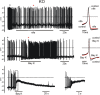
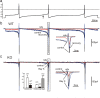
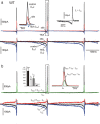
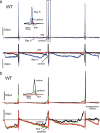
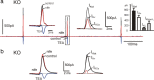
We studied wild-type (WT) and Cav1.3(-/-) mouse chromaffin cells (MCCs) with the aim to determine the isoform of L-type Ca(2+) channel (LTCC) and BK channels that underlie the pacemaker current controlling spontaneous firing. Most WT-MCCs (80%) were spontaneously active (1.5 Hz) and highly sensitive to nifedipine and BayK-8644 (1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid, methyl ester). Nifedipine blocked the firing, whereas BayK-8644 increased threefold the firing rate. The two dihydropyridines and the BK channel blocker paxilline altered the shape of action potentials (APs), suggesting close coupling of LTCCs to BK channels. WT-MCCs expressed equal fractions of functionally active Cav1.2 and Cav1.3 channels. Cav1.3 channel deficiency decreased the number of normally firing MCCs (30%; 2.0 Hz), suggesting a critical role of these channels on firing, which derived from their slow inactivation rate, sizeable activation at subthreshold potentials, and close coupling to fast inactivating BK channels as determined by using EGTA and BAPTA Ca(2+) buffering. By means of the action potential clamp, in TTX-treated WT-MCCs, we found that the interpulse pacemaker current was always net inward and dominated by LTCCs. Fast inactivating and non-inactivating BK currents sustained mainly the afterhyperpolarization of the short APs (2-3 ms) and only partially the pacemaker current during the long interspike (300-500 ms). Deletion of Cav1.3 channels reduced drastically the inward Ca(2+) current and the corresponding Ca(2+)-activated BK current during spikes. Our data highlight the role of Cav1.3, and to a minor degree of Cav1.2, as subthreshold pacemaker channels in MCCs and open new interesting features about their role in the control of firing and catecholamine secretion at rest and during sustained stimulations matching acute stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low pHo boosts burst firing and catecholamine release by blocking TASK-1 and BK channels while preserving Cav1 channels in mouse chromaffin cells.J Physiol. 2017 Apr 15;595(8):2587-2609. doi: 10.1113/JP273735. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28026020 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced availability of voltage-gated sodium channels by depolarization or blockade by tetrodotoxin boosts burst firing and catecholamine release in mouse chromaffin cells.J Physiol. 2015 Feb 15;593(4):905-27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.283374. Epub 2015 Jan 26. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25620605 Free PMC article.
-
CaV1.3 as pacemaker channels in adrenal chromaffin cells: specific role on exo- and endocytosis?Channels (Austin). 2010 Nov-Dec;4(6):440-6. doi: 10.4161/chan.4.6.12866. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Channels (Austin). 2010. PMID: 21084859 Review.
-
Activation of BK channels in rat chromaffin cells requires summation of Ca(2+) influx from multiple Ca(2+) channels.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Sep;84(3):1123-35. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.3.1123. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10979988
-
Ca(v)1.3 and BK channels for timing and regulating cell firing.Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Dec;42(3):185-98. doi: 10.1007/s12035-010-8151-3. Epub 2010 Nov 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 21088933 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylmercury decreases cellular excitability by a direct blockade of sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells: an integrative study.Pflugers Arch. 2013 Dec;465(12):1727-40. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1311-3. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 23821297
-
PACAP and acetylcholine cause distinct Ca2+ signals and secretory responses in chromaffin cells.J Gen Physiol. 2023 Feb 6;155(2):e202213180. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202213180. Epub 2022 Dec 20. J Gen Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36538657 Free PMC article.
-
High signal-to-noise imaging of spontaneous and 5 ns electric pulse-evoked Ca2+ signals in GCaMP6f-expressing adrenal chromaffin cells isolated from transgenic mice.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 31;18(3):e0283736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283736. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37000822 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal clustering between BK and CaV1.3 channels promotes functional coupling and BK channel activation at low voltage.Elife. 2017 Jun 30;6:e28029. doi: 10.7554/eLife.28029. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28665272 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for PKC signaling in chromaffin cell exocytosis.Biophys J. 2025 Jun 3;124(11):1785-1797. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.12.005. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Biophys J. 2025. PMID: 39639770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldelli P, Hernández-Guijo JM, Carabelli V, Novara M, Cesetti T, Andrés-Mateos E, Montiel C, Carbone E. Direct and remote modulation of L-channels in chromaffin cells: distinct actions on alpha1C and alpha1D subunits? Mol Neurobiol. 2004;29:73–96. - PubMed
-
- Bean BP. The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:451–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
