Predominant clonal accumulation of CD8+ T cells with moderate avidity in the central nervous systems of Theiler's virus-infected C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 20071578
- PMCID: PMC2826044
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01948-09
Predominant clonal accumulation of CD8+ T cells with moderate avidity in the central nervous systems of Theiler's virus-infected C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
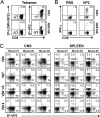
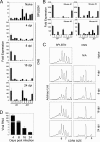
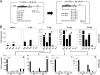
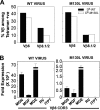
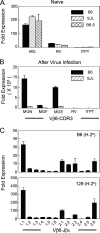
Induction of antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells bearing a high-avidity T-cell receptor (TCR) is thought to be an important factor in antiviral and antitumor immune responses. However, the relationship between TCR diversity and functional avidity of epitope-specific CD8(+) T cells accumulating in the central nervous system (CNS) during viral infection is unknown. Hence, analysis of T-cell diversity at the clonal level is important to understand the fate and function of virus-specific CD8(+) T cells. In this study, we examined the Vbeta diversity and avidity of CD8(+) T cells specific to the predominant epitope (VP2(121-130)) of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. We found that Vbeta6(+) CD8(+) T cells, associated with epitope specificity, predominantly expanded in the CNS during viral infection. Further investigations of antigen-specific Vbeta6(+) CD8(+) T cells by CDR3 spectratyping and sequencing indicated that distinct T-cell clonotypes are preferentially increased in the CNS compared to the periphery. Among the epitope-specific Vbeta6(+) CD8(+) T cells, MGX-Jbeta1.1 motif-bearing cells, which could be found at a high precursor frequency in naïve mice, were expanded in the CNS and tightly associated with gamma interferon production. These T cells displayed moderate avidity for the cognate epitope rather than the high avidity normally observed in memory/effector T cells. Therefore, our findings provide new insights into the CD8(+) T-cell repertoire during immune responses to viral infection in the CNS.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander-Miller, M. A. 2005. High-avidity CD8+ T cells: optimal soldiers in the war against viruses and tumors. Immunol. Res. 31:13-24. - PubMed
-
- Altman, J. D., P. A. Moss, P. J. Goulder, D. H. Barouch, M. G. McHeyzer-Williams, J. I. Bell, A. J. McMichael, and M. M. Davis. 1996. Phenotypic analysis of antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Science 274:94-96. - PubMed
-
- Babbe, H., A. Roers, A. Waisman, H. Lassmann, N. Goebels, R. Hohlfeld, M. Friese, R. Schroder, M. Deckert, S. Schmidt, R. Ravid, and K. Rajewsky. 2000. Clonal expansions of CD8(+) T cells dominate the T cell infiltrate in active multiple sclerosis lesions as shown by micromanipulation and single cell polymerase chain reaction. J. Exp. Med. 192:393-404. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blackman, M. A., H. Gerhard-Burgert, D. L. Woodland, E. Palmer, J. W. Kappler, and P. Marrack. 1990. A role for clonal inactivation in T cell tolerance to Mls-1a. Nature 345:540-542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

