Effective and selective targeting of leukemia cells using a TORC1/2 kinase inhibitor
- PMID: 20072130
- PMCID: PMC4017764
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2091
Effective and selective targeting of leukemia cells using a TORC1/2 kinase inhibitor
Abstract
Targeting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) protein is a promising strategy for cancer therapy. The mTOR kinase functions in two complexes, TORC1 (target of rapamycin complex-1) and TORC2 (target of rapamycin complex-2); however, neither of these complexes is fully inhibited by the allosteric inhibitor rapamycin or its analogs. We compared rapamycin with PP242, an inhibitor of the active site of mTOR in both TORC1 and TORC2 (hereafter referred to as TORC1/2), in models of acute leukemia harboring the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) translocation. We demonstrate that PP242, but not rapamycin, causes death of mouse and human leukemia cells. In vivo, PP242 delays leukemia onset and augments the effects of the current front-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors more effectively than does rapamycin. Unexpectedly, PP242 has much weaker effects than rapamycin on the proliferation and function of normal lymphocytes. PI-103, a less selective TORC1/2 inhibitor that also targets phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), is more immunosuppressive than PP242. These findings establish that Ph(+) transformed cells are more sensitive than normal lymphocytes to selective TORC1/2 inhibitors and support the development of such inhibitors for leukemia therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
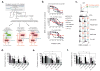


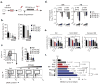
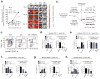
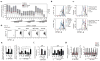
Similar articles
-
Effective targeting of colorectal cancer cells using TORC1/2 kinase inhibitors in vitro and in vivo.Future Oncol. 2016 Feb;12(4):515-24. doi: 10.2217/fon.15.248. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26776341
-
Targeting TORC2 in multiple myeloma with a new mTOR kinase inhibitor.Blood. 2010 Nov 25;116(22):4560-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-285726. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20686120 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR kinase inhibitor pp242 causes mitophagy terminated by apoptotic cell death in E1A-Ras transformed cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44905-26. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6457. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26636543 Free PMC article.
-
New inhibitors of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway: insights into mTOR signaling from a new generation of Tor Kinase Domain Inhibitors (TORKinibs).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;347:241-62. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_64. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20549474 Review.
-
Target of rapamycin signaling in leukemia and lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Nov 15;16(22):5374-80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0480. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20826559 Review.
Cited by
-
SNS-032 inhibits mTORC1/mTORC2 activity in acute myeloid leukemia cells and has synergistic activity with perifosine against Akt.J Hematol Oncol. 2013 Feb 18;6:18. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-18. J Hematol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23415012 Free PMC article.
-
Fargesin Inhibits EGF-Induced Cell Transformation and Colon Cancer Cell Growth by Suppression of CDK2/Cyclin E Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 19;22(4):2073. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042073. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669811 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of mTORC2 may have advantages over selective targeting of mTORC1 in the treatment of malignant pheochromocytoma.Tumour Biol. 2015 Jul;36(7):5273-81. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3187-7. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25666752
-
Intersection of mTOR and STAT signaling in immunity.Trends Immunol. 2015 Jan;36(1):21-9. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Trends Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25592035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting of mTOR catalytic site inhibits multiple steps of the HIV-1 lifecycle and suppresses HIV-1 viremia in humanized mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 28;112(30):9412-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1511144112. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26170311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:606–619. - PubMed
-
- Samuels Y, Ericson K. Oncogenic PI3K and its role in cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2006;18:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Martelli AM, et al. Involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway in the resistance to therapeutic treatments of human leukemias. Histol Histopathol. 2005;20:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Wee S, et al. PI3K pathway activation mediates resistance to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant cancers. Cancer Res. 2009;69:4286–4293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

