Synergistic and additive effects of epigallocatechin gallate and digitonin on Plasmodium sporozoite survival and motility
- PMID: 20072627
- PMCID: PMC2800191
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008682
Synergistic and additive effects of epigallocatechin gallate and digitonin on Plasmodium sporozoite survival and motility
Abstract
Background: Most medicinal plants contain a mixture of bioactive compounds, including chemicals that interact with intracellular targets and others that can act as adjuvants to facilitate absorption of polar agents across cellular membranes. However, little is known about synergistic effects between such potential drug candidates and adjuvants. To probe for such effects, we tested the green tea compound epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and the membrane permeabilising digitonin on Plasmodium sporozoite motility and viability.
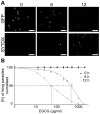
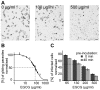
Methodology/principal findings: Green fluorescent P. berghei sporozoites were imaged using a recently developed visual screening methodology. Motility and viability parameters were automatically analyzed and IC50 values were calculated, and the synergism of drug and adjuvant was assessed by the fractional inhibitory concentration index. Validating our visual screening procedure, we showed that sporozoite motility and liver cell infection is inhibited by EGCG at nontoxic concentrations. Digitonin synergistically increases the cytotoxicity of EGCG on sporozoite survival, but shows an additive effect on sporozoite motility.
Conclusions/significance: We proved the feasibility of performing highly reliable visual screens for compounds against Plasmodium sporozoites. We thereby could show an advantage of administering mixtures of plant metabolites on inhibition of cell motility and survival. Although the effective concentration of both drugs is too high for use in malaria prophylaxis, the demonstration of a synergistic effect between two plant compounds could lead to new avenues in drug discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

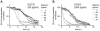


References
-
- Wink M. Evolutionary advantage and molecular modes of action of multi-component mixtures used in phytomedicine. Curr Drug Med. 2008;9:996–1009. - PubMed
-
- Wink M. Kayser O, Quax W, editors. Bioprospecting: The search for bioactive lead structures from nature. 2007. pp. 97–116. Medicinal Plant Biotechnology. Wiley-VCH.
-
- Schäfer H, Wink M. Medicinally important secondary metabolites in recombinant microorganisms or plants: Progress in alkaloid biosynthesis. Biotechnol J. 2009;4:1684–1703. - PubMed
-
- Harborne JB. Role of secondary metabolites in chemical defence mechanisms in plants. Ciba Found Symp. 1990;154:126–134. - PubMed
-
- Waterman PG. Roles for secondary metabolites in plants. Ciba Found Symp. 1992;171:255–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

