The p38 MAPK regulates IL-24 expression by stabilization of the 3' UTR of IL-24 mRNA
- PMID: 20072629
- PMCID: PMC2801610
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008671
The p38 MAPK regulates IL-24 expression by stabilization of the 3' UTR of IL-24 mRNA
Abstract
Background: IL-24 (melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 (mda-7)), a member of the IL-10 cytokine family, possesses the properties of a classical cytokine as well as tumor suppressor effects. The exact role of IL-24 in the immune system has not been defined but studies have indicated a role for IL-24 in inflammatory conditions such as psoriasis. The tumor suppressor effects of IL-24 include inhibition of angiogenesis, sensitization to chemotherapy, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-mediated apoptosis. Current knowledge on the regulation of IL-24 expression is sparse. Previous studies have suggested that mRNA stabilization is of major importance to IL-24 expression. Yet, the mechanisms responsible for the regulation of IL-24 mRNA stability remain unidentified. As p38 MAPK is known to regulate gene expression by interfering with mRNA degradation we examined the role of p38 MAPK in the regulation of IL-24 gene expression in cultured normal human keratinocytes.
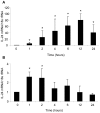
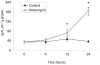
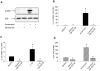
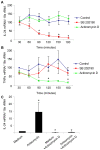
Methodology/principal findings: In the present study we show that anisomycin- and IL-1beta- induced IL-24 expression is strongly dependent on p38 MAPK activation. Studies of IL-24 mRNA stability in anisomycin-treated keratinocytes reveal that the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB 202190 accelerates IL-24 mRNA decay suggesting p38 MAPK to regulate IL-24 expression by mRNA-stabilizing mechanisms. The insertion of the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of IL-24 mRNA in a tet-off reporter construct induces degradation of the reporter mRNA. The observed mRNA degradation is markedly reduced when a constitutively active mutant of MAPK kinase 6 (MKK6), which selectively activates p38 MAPK, is co-expressed.
Conclusions/significance: Taken together, we here report p38 MAPK as a regulator of IL-24 expression and determine interference with destabilization mediated by the 3' UTR of IL-24 mRNA as mode of action. As discussed in the present work these findings have important implications for our understanding of IL-24 as a tumor suppressor protein as well as an immune modulating cytokine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene. 1995;11:2477–2486. - PubMed
-
- Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Lebedeva IV, et al. MDA-7/IL-24: novel cancer growth suppressing and apoptosis inducing cytokine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14:35–51. - PubMed
-
- Wang M, Tan Z, Zhang R, Kotenko SV, Liang P. Interleukin 24 (MDA-7/MOB-5) signals through two heterodimeric receptors, IL-22R1/IL-20R2 and IL-20R1/IL-20R2. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:7341–7347. - PubMed
-
- Dumoutier L, Leemans C, Lejeune D, Kotenko SV, Renauld JC. Cutting edge: STAT activation by IL-19, IL-20 and mda-7 through IL-20 receptor complexes of two types. J Immunol. 2001;167:3545–3549. - PubMed
-
- Ekmekcioglu S, Ellerhorst J, Mhashilkar AM, Sahin AA, Read CM, et al. Down-regulated melanoma differentiation associated gene (mda-7) expression in human melanomas. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:54–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

