Intraocular pressure profile during the modified diurnal tension curve using Goldman applanation tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry
- PMID: 20072644
- PMCID: PMC2802501
- DOI: 10.1007/s12177-009-9016-8
Intraocular pressure profile during the modified diurnal tension curve using Goldman applanation tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry
Abstract
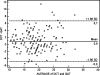
The aim of this study was to compare the intraocular pressure (IOP) profile during the modified diurnal tension curve (mDTC) using Goldman applanation tonometry (GAT) and dynamic contour tonometry (DCT) in treated glaucomatous eyes. Eligible subjects were submitted to the mDTC using GAT and DCT in this sequence. IOP measurements were performed at 8 a.m., 10 a.m., 2 p.m., and 4 p.m.. Central corneal thickness was measured using ultrasound pachymetry in the morning. Statistical analysis was performed using paired Student's t test and Bland-Altman plot. The mean difference between DCT and GAT measurements was 0.9 mmHg. The mean +/- SD IOP measurements during the mDTC were 19.68 +/- 4.68, 17.63 +/- 4.44, 17.25 +/- 5.41, and 17.32 +/- 4.25 mmHg using GAT and 19.97 +/- 4.75, 18.79 +/- 4.61, 19.53 +/- 5.30, and 19.43 +/- 5.45 mmHg using DCT. IOP measurements were higher in the morning (8 a.m.) and decreased throughout the day using both tonometers. The difference between IOP measurements using GAT and DCT was smaller in the morning and increased throughout the day. The IOP variability using GAT was higher than using DCT. Corneal biomechanical properties might help explain our findings.
Keywords: Corneal biomechanics; Dynamic contour tonometry; Glaucoma; Intraocular pressure; Tension curves.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of Goldmann applanation tonometry, rebound tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry in normal and glaucomatous eyes.Int J Ophthalmol. 2015 Apr 18;8(2):299-304. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.02.15. eCollection 2015. Int J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25938044 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of corneal thickness on dynamic contour, rebound, and goldmann tonometry.Ophthalmology. 2006 Dec;113(12):2156-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.06.016. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Ophthalmology. 2006. PMID: 16996599 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Goldmann and Pascal tonometry in relation to corneal hysteresis and central corneal thickness in nonglaucomatous eyes.Clin Ophthalmol. 2011;5:1071-7. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S23086. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Clin Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21847339 Free PMC article.
-
[Dynamic Contour Tonometry and Goldmann Applanation Tonometry: Difference of Intraocular Pressure Values Between Eyes with and without Glaucomatous Damage in Thin Corneas].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2015 Oct;232(10):1190-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-104772. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2015. PMID: 26512850 German.
-
Tonometry in corneal edema after cataract surgery: dynamic contour tonometry versus Goldmann applanation tonometry.Clin Ophthalmol. 2013;7:815-9. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S44412. Epub 2013 May 3. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23662041 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Laser speckle flowgraphy derived characteristics of optic nerve head perfusion in normal tension glaucoma and healthy individuals: a Pilot study.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 28;8(1):5343. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23149-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29593269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leske MC, Heijl A, Hussein M, Early Manifest GlaucomaTrial Group et al. Factors for glaucoma progression and the effect of treatment: the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121:48–56. - PubMed
-
- Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ, Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study Group et al. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:701–713. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
