Hepatitis C virus induces oxidative stress, DNA damage and modulates the DNA repair enzyme NEIL1
- PMID: 20074151
- PMCID: PMC3565844
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06128.x
Hepatitis C virus induces oxidative stress, DNA damage and modulates the DNA repair enzyme NEIL1
Abstract
Background and aims: Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-induced chronic inflammation may induce oxidative stress which could compromise the repair of damaged DNA, rendering cells more susceptible to spontaneous or mutagen-induced alterations, the underlying cause of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. In the current study we examined the induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) resulting from HCV infection and evaluated its effect on the host DNA damage and repair machinery.
Methods: HCV infected human hepatoma cells were analyzed to determine (i) ROS, (ii) 8-oxoG and (iii) DNA glycosylases NEIL1, NEIL2, OGG1. Liver biopsies were analyzed for NEIL1.
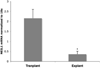
Results: Human hepatoma cells infected with HCV JFH-1 showed 30-60-fold increases in ROS levels compared to uninfected cells. Levels of the oxidatively modified guanosine base 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) were significantly increased sixfold in the HCV-infected cells. Because DNA glycosylases are the enzymes that remove oxidized nucleotides, their expression in HCV-infected cells was analyzed. NEIL1 but not OGG1 or NEIL2 gene expression was impaired in HCV-infected cells. In accordance, we found reduced glycosylase (NEIL1-specific) activity in HCV-infected cells. The antioxidant N-acetyl cystein (NAC) efficiently reversed the NEIL1 repression by inhibiting ROS induction by HCV. NEIL1 expression was also partly restored when virus-infected cells were treated with interferon (IFN). HCV core and to a lesser extent NS3-4a and NS5A induced ROS, and downregulated NEIL1 expression. Liver biopsy specimens showed significant impairment of NEIL1 levels in HCV-infected patients with advanced liver disease compared to patients with no disease.
Conclusion: Collectively, the data indicate that HCV induction of ROS and perturbation of NEIL1 expression may be mechanistically involved in progression of liver disease and suggest that antioxidant and antiviral therapies can reverse these deleterious effects of HCV in part by restoring function of the DNA repair enzyme/s.
Figures
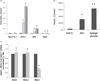
 , HUH7.5.1;
, HUH7.5.1;  , JFH-1.
, JFH-1.
 , 24 h;
, 24 h;  , 48 h;
, 48 h;  , 72 h. (b) Left to right lanes: total cell extracts were isolated from mock-infected Huh7.5.1 cells, Huh7.5.1 cells infected with HCV JFH-1, HCV-infected Huh7.5.1 cells treated with IFN (100 U/mL) and N-acetyl cystein (NAC; 10 µM) at the time of infection, separated by sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and levels of HCV core (top bands), NEIL1 (middle bands) and control glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) proteins (lower bands) were detected by western blot analysis. Densitometric scan shows NEIL1 fold decrease. (c) Impaired strand incision activity of NEIL1 DNA glycosylase. 32-P labeled 51-mer 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) containing bubble oligonucleotides was used as substrate. Lanes 1 and 4, cellular extracts of mock-infected Huh7.5.1 cells and no extract, respectively; lanes 2 and 3, cellular extracts of Huh7.5.1 cells infected with HCV JFH-1 at 48 and 72 h, respectively. In all cases, graphical representation of the NEIL1-specific incision or cleavage product percentage normalized to Lane 4 (no extract reaction) is depicted, showing averages of three experiments. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.001).
, 72 h. (b) Left to right lanes: total cell extracts were isolated from mock-infected Huh7.5.1 cells, Huh7.5.1 cells infected with HCV JFH-1, HCV-infected Huh7.5.1 cells treated with IFN (100 U/mL) and N-acetyl cystein (NAC; 10 µM) at the time of infection, separated by sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and levels of HCV core (top bands), NEIL1 (middle bands) and control glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) proteins (lower bands) were detected by western blot analysis. Densitometric scan shows NEIL1 fold decrease. (c) Impaired strand incision activity of NEIL1 DNA glycosylase. 32-P labeled 51-mer 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) containing bubble oligonucleotides was used as substrate. Lanes 1 and 4, cellular extracts of mock-infected Huh7.5.1 cells and no extract, respectively; lanes 2 and 3, cellular extracts of Huh7.5.1 cells infected with HCV JFH-1 at 48 and 72 h, respectively. In all cases, graphical representation of the NEIL1-specific incision or cleavage product percentage normalized to Lane 4 (no extract reaction) is depicted, showing averages of three experiments. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.001).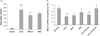
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

