Pattern of P450 expression at the human blood-brain barrier: roles of epileptic condition and laminar flow
- PMID: 20074231
- PMCID: PMC3386640
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02428.x
Pattern of P450 expression at the human blood-brain barrier: roles of epileptic condition and laminar flow
Abstract
Purpose: P450 enzymes (CYPs) play a major role in hepatic drug metabolism. It is unclear whether these enzymes are functionally expressed by the diseased human blood-brain barrier (BBB) and are involved in local drug metabolism or response. We have evaluated the cerebrovascular CYP expression and function, hypothesizing possible implication in drug-resistant epilepsy.
Methods: CYP P450 transcript levels were assessed by cDNA microarray in primary endothelial cultures established from a cohort of brain resections (n = 12, drug-resistant epilepsy EPI-EC and aneurism domes ANE-EC). A human brain endothelial cell line (HBMEC) and non-brain endothelial cell line (HUVEC) were used as controls. The effect of exposure to shear stress on CYP expression was evaluated. Results were confirmed by Western blot and immunohistochemistry on brain specimens. Endothelial drug metabolism was assessed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC-UV).
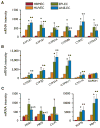
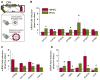
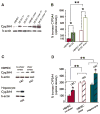
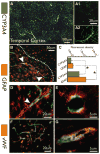
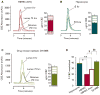
Results: cDNA microarray showed the presence of CYP enzymes in isolated human primary brain endothelial cells. Using EPI-EC and HBMEC we found that CYP mRNA levels were significantly affected by exposure to shear stress. CYP3A4 protein was overexpressed in EPI-EC (290 ± 30%) compared to HBMEC and further upregulated by shear stress exposure. CYP3A4 was increased in the vascular compartment at regions of reactive gliosis in the drug-resistant epileptic brain. Metabolism of carbamazepine was significantly elevated in EPI-EC compared to HBMEC.
Discussion: These results support the hypothesis of local drug metabolism at the diseased BBB. The direct association between BBB CYP enzymes and the drug-resistant phenotype needs to be further investigated.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2010 International League Against Epilepsy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of pregnane X and glucocorticoid receptors and the regulation of cytochrome P450 in human epileptic brain endothelial cells.Epilepsia. 2017 Apr;58(4):576-585. doi: 10.1111/epi.13703. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28199000 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and functional relevance of UGT1A4 in a cohort of human drug-resistant epileptic brains.Epilepsia. 2013 Sep;54(9):1562-70. doi: 10.1111/epi.12318. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Epilepsia. 2013. PMID: 23865846 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of glucocorticoid receptor in human epileptic endothelial cells impacts drug biotransformation in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model.Epilepsia. 2018 Nov;59(11):2049-2060. doi: 10.1111/epi.14567. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Epilepsia. 2018. PMID: 30264400 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of cytochrome p450 in brain drug metabolism.Curr Drug Metab. 2007 May;8(4):297-306. doi: 10.2174/138920007780655478. Curr Drug Metab. 2007. PMID: 17504219 Review.
-
The unique regulation of brain cytochrome P450 2 (CYP2) family enzymes by drugs and genetics.Drug Metab Rev. 2004 May;36(2):313-33. doi: 10.1081/dmr-120034149. Drug Metab Rev. 2004. PMID: 15237857 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic 3D On-Chip BBB Model Design, Development, and Applications in Neurological Diseases.Cells. 2021 Nov 15;10(11):3183. doi: 10.3390/cells10113183. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breaking Bad: the Structure and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Epilepsy.AAPS J. 2017 Jul;19(4):973-988. doi: 10.1208/s12248-017-0096-2. Epub 2017 May 26. AAPS J. 2017. PMID: 28550637 Review.
-
12/15-lipoxygenase mediates disturbed flow-induced endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis.Mol Med. 2025 Jul 15;31(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01297-0. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40660143 Free PMC article.
-
CYP1B1-RMDN2 Alzheimer's disease endophenotype locus identified for cerebral tau PET.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 20;15(1):8251. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52298-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39304655 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional microenvironment regulates gene expression, function, and tight junction dynamics of iPSC-derived blood-brain barrier microvessels.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022 Nov 5;19(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12987-022-00377-1. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022. PMID: 36333694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Khan EU, Rollinson CM, Reichel A, Janigro D, Dombrowski SM, Dobbie MS, Begley DJ. Drug resistance in epilepsy: the role of the blood-brain barrier. Novartis Found Symp. 2002;243:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Arisaka T, Mitsumata M, Kawasumi M, Tohjima T, Hirose S, Yoshida Y. Effects of shear stress on glycosaminoglycan synthesis in vascular endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995;748:543–554. - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Gorter JA, Ramkema M, Redeker S, Ozbas-Gerceker F, van Vliet EA, Scheffer GL, Scheper RJ, van der Valk P, Baayen JC, Troost D. Expression and cellular distribution of multidrug resistance-related proteins in the hippocampus of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2004;45:441–451. - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Gorter JA. Gene expression profile in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscientist. 2007;13:100–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

