miRMaid: a unified programming interface for microRNA data resources
- PMID: 20074352
- PMCID: PMC2831003
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-29
miRMaid: a unified programming interface for microRNA data resources
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small RNAs that play a key role in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in animals and plants. The number of known miRNAs has increased rapidly over the years. The current release (version 14.0) of miRBase, the central online repository for miRNA annotation, comprises over 10.000 miRNA precursors from 115 different species. Furthermore, a large number of decentralized online resources are now available, each contributing with important miRNA annotation and information.
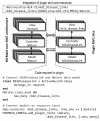
Results: We have developed a software framework, designated here as miRMaid, with the goal of integrating miRNA data resources in a uniform web service interface that can be accessed and queried by researchers and, most importantly, by computers. miRMaid is built around data from miRBase and is designed to follow the official miRBase data releases. It exposes miRBase data as inter-connected web services. Third-party miRNA data resources can be modularly integrated as miRMaid plugins or they can loosely couple with miRMaid as individual entities in the World Wide Web. miRMaid is available as a public web service but is also easily installed as a local application. The software framework is freely available under the LGPL open source license for academic and commercial use.
Conclusion: miRMaid is an intuitive and modular software platform designed to unify miRBase and independent miRNA data resources. It enables miRNA researchers to computationally address complex questions involving the multitude of miRNA data resources. Furthermore, miRMaid constitutes a basic framework for further programming in which microRNA-interested bioinformaticians can readily develop their own tools and data sources.
Figures




References
-
- Medina PP, Slack FJ. microRNAs and cancer: an overview. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2485–2492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

