Type I gamma phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase modulates invasion and proliferation and its expression correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer
- PMID: 20074374
- PMCID: PMC2880426
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2471
Type I gamma phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase modulates invasion and proliferation and its expression correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: The loss of E-cadherin based cell-cell contacts and tumor cell migration to the vasculature and lymphatic system are hallmarks of metastasis of epithelial cancers. Type I gamma phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase (PIPKIgamma), an enzyme that generates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI4,5P2) a lipid messenger and precursor to many additional second messengers, was found to regulate E-cadherin cell-cell contacts and growth factor-stimulated directional cell migration, indicating that PIPKIgamma regulates key steps in metastasis. Here, we assess the expression of PIPKIgamma in breast cancers and have shown that expression correlated with disease progression and outcome.
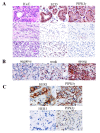
Methods: Using a tissue microarray, we analyzed 438 breast carcinomas for the levels of PIPKIgamma and investigated the correlation of PIPKIgamma expression with patient survival via Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. Moreover, via knockdown of the expression of PIPKIgamma in cultured breast cancer cells with siRNA, the roles of PIPKIgamma in breast cancer migration, invasion, and proliferation were examined.
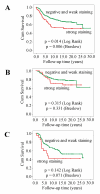
Results: Tissue microarray data shows that approximately 18% of the cohort immunostained showed high expression of PIPKIgamma. The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed a significant inverse correlation between strong PIPKIgamma expression and overall patient survival. Expression of PIPKIgamma correlated positively with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression, which regulates breast cancer progression and metastasis. In cultured breast cancer cells, PIPKIgamma is required for growth factor stimulated migration, invasion, and proliferation of cells.
Conclusions: The results reveal a significant correlation between PIPKIgamma expression and the progression of breast cancer. This is consistent with PIPKIgamma 's role in breast cancer cell migration, invasion, and proliferation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase inhibits breast cancer metastasis.Oncogene. 2015 Aug 27;34(35):4635-46. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.393. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25486426 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase suppresses ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jul;38(1):253-262. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5670. Epub 2017 May 25. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28560454 Free PMC article.
-
Type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase promotes tumor growth by facilitating Warburg effect in colorectal cancer.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jun;44:375-386. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.015. Epub 2019 May 16. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31105034 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-induced phosphorylation of type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase promotes pancreatic cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(26):42621-42637. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16730. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28388589 Free PMC article.
-
IQGAP1 is a novel phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate effector in regulation of directional cell migration.EMBO J. 2013 Oct 2;32(19):2617-30. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.191. Epub 2013 Aug 27. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23982733 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Human β-Defensin 2 (HBD-2) Displays Oncolytic Activity but Does Not Affect Tumour Cell Migration.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 6;12(2):264. doi: 10.3390/biom12020264. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204765 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion in the tumour metastasis: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic targets.Biomark Res. 2025 Mar 5;13(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00745-7. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 40045379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoinositide signaling regulates the exocyst complex and polarized integrin trafficking in directionally migrating cells.Dev Cell. 2012 Jan 17;22(1):116-30. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.10.030. Dev Cell. 2012. PMID: 22264730 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol phosphate 5-kinase Iγi2 in association with Src controls anchorage-independent growth of tumor cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 29;288(48):34707-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.512848. Epub 2013 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24151076 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of NRF2 by stably associated phosphoinositides and small heat shock proteins in response to stress.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jul;301(7):110367. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110367. Epub 2025 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40516875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paulson KE, Rieger-Christ K, McDevitt MA, Kuperwasser C, Kim J, Unanue VE, Zhang X, Hu M, Ruthazer R, Berasi SP, Huang CY, Giri D, Kaufman S, Dugan JM, Blum J, Netto G, Wazer DE, Summerhayes IC, Yee AS. Alterations of the HBP1 transcriptional repressor are associated with invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6136–6145. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0567. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

