GnRH I and II up-regulate MMP-26 expression through the JNK pathway in human cytotrophoblasts
- PMID: 20074375
- PMCID: PMC2819245
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-8-5
GnRH I and II up-regulate MMP-26 expression through the JNK pathway in human cytotrophoblasts
Abstract
Background: Matrix metalloproteinase-26 (MMP-26), one of the main mediators of extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, has been shown to exist in trophoblasts of human placenta and to play a role in trophoblast cell invasion. However, little is known about the regulation of MMP-26 expression in human trophoblasts. Recently, gonadotropin-releasing hormone I (GnRH I) and GnRH II have been shown to regulate the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1), and urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA)/plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI) in human trophoblasts, suggesting that these two hormones may work as paracrine and/or autocrine regulators in modulating the activities of various protease systems at the feto-maternal interface. In this study, we determined the regulatory effects of GnRH I and GnRH II on the expression of MMP-26 in human immortalized cytotrophoblast-like cell line, B6Tert-1.
Methods: Real-time PCR was used to quantify mRNA levels of MMP-26 in human trophoblast-like cell line, B6Tert-1 and primary cultured cytotrophoblasts. Western blotting was used to characterize the expression of MMP-26 and the phosphorylation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) in B6Tert-1 cells after treatment with GnRH I and GnRH II.
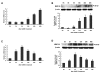
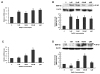
Results: We found that GnRH I increased MMP-26 expression in B6Tert-1 cells after 12 h of treatment at both the mRNA and protein level, while GnRH II increased MMP-26 expression beginning at 3 h of treatment. Treatment of GnRH I at 1 nM resulted in maximal increase of MMP-26 mRNA and protein levels, whereas GnRH II treatment at a concentration of 100 nM was required to induce maximal increase in MMP-26 expression. In addition, we demonstrated that the activation of JNK, but not ERK1/2, was required for GnRH I and II-stimulated MMP-26 production in B6Tert-1 cells and primary cytotrophoblasts.
Conclusions: These novel findings indicated that GnRH I and II could up-regulate MMP-26 expression through the JNK signaling pathway in human trophoblast-like/trophoblast cells.
Figures
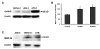
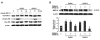
Similar articles
-
Promotion of human trophoblasts invasion by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) I and GnRH II via distinct signaling pathways.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jul;23(7):1014-21. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0451. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19372239 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) I and GnRH II on the levels of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in primary cultures of human extravillous cytotrophoblasts.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Oct;88(10):4781-90. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030659. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 14557455
-
The effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) I and GnRH II on the urokinase-type plasminogen activator/plasminogen activator inhibitor system in human extravillous cytotrophoblasts in vitro.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Dec;87(12):5594-603. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-020883. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12466358
-
Interleukin-10 may participate in regulating trophoblast invasion in human placentae throughout gestation.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008 Jul;60(1):19-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2008.00586.x. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18593434
-
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone promotes ovarian cancer cell invasiveness through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated activation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9.Cancer Res. 2006 Nov 15;66(22):10902-10. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2217. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17108127
Cited by
-
Reproductive Outcomes of Dual Trigger versus hCG Alone in Women Undergoing In Vitro Fertilization with Fresh Embryo Transfer Cycles.Obstet Gynecol Int. 2024 Jul 9;2024:9972437. doi: 10.1155/2024/9972437. eCollection 2024. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2024. PMID: 39015476 Free PMC article.
-
Final follicular maturation by administration of GnRH agonist plus HCG versus HCG in normal responders in ART cycles: An RCT.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2017 Jul;15(7):429-434. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2017. PMID: 29177244 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the immunomodulatory regulation of matrix metalloproteinase at the maternal-fetal interface during early pregnancy and pregnancy-related diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1067661. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1067661. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36700222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney-Replenishing Herb Induces SOCS-3 Expression via ERK/MAPK Pathway and Improves Growth of the First-Trimester Human Trophoblast Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:2473431. doi: 10.1155/2017/2473431. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29234375 Free PMC article.
-
dNK cells facilitate the interaction between trophoblastic and endothelial cells via VEGF-C and HGF.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Sep;95(8):695-704. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.45. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28653669
References
-
- Aplin JD. Implantation, trophoblast differentiation and haemochorial placentation: mechanistic evidence in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1991;99:681–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

