Cystatin E/M suppresses legumain activity and invasion of human melanoma
- PMID: 20074384
- PMCID: PMC2822816
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-17
Cystatin E/M suppresses legumain activity and invasion of human melanoma
Abstract
Background: High activity of cysteine proteases such as legumain and the cathepsins have been shown to facilitate growth and invasion of a variety of tumor types. In breast cancer, several recent studies have indicated that loss of the cysteine protease inhibitor cystatin E/M leads to increased growth and metastasis. Although cystatin E/M is normally expressed in the skin, its role in cysteine protease regulation and progression of malignant melanoma has not been studied.
Methods: A panel of various non-melanoma and melanoma cell lines was used. Cystatin E/M and C were analyzed in cell media by immunoblotting and ELISA. Legumain, cathepsin B and L were analyzed in cell lysates by immunoblotting and their enzymatic activities were analyzed by peptide substrates. Two melanoma cell lines lacking detectable secretion of cystatin E/M were transfected with a cystatin E/M expression plasmid (pCST6), and migration and invasiveness were studied by a Matrigel invasion assay.
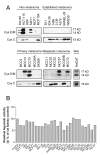
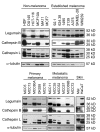
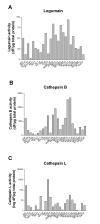
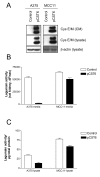
Results: Cystatin E/M was undetectable in media from all established melanoma cell lines examined, whereas strong immunobands were detected in two of five primary melanoma lines and in two of six lines derived from patients with metastatic disease. Among the four melanoma lines secreting cystatin E/M, the glycosylated form (17 kD) was predominant compared to the non-glycosylated form (14 kD). Legumain, cathepsin B and L were expressed and active in most of the cell lines, although at low levels in the melanomas expressing cystatin E/M. In the melanoma lines where cystatin E/M was secreted, cystatin C was generally absent or expressed at a very low level. When melanoma cells lacking secretion of cystatin E/M were transfected with pCST6, their intracellular legumain activity was significantly inhibited. In contrast, cathepsin B activity was not affected. Furthermore, invasion was suppressed in cystatin E/M over-expressing melanoma cell lines as measured by the transwell Matrigel assay.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the level of cystatin E/M regulates legumain activity and hence the invasive potential of human melanoma cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low-level internalization of cystatin E/M affects legumain activity and migration of melanoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 1;292(35):14413-14424. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.776138. Epub 2017 Jun 19. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28630039 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of cystatin M in metastatic oral cancer cell line MDA-686Ln by siRNA increases cysteine proteinases and legumain activities, cell proliferation and in vitro invasion.Life Sci. 2006 Jan 18;78(8):898-907. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.05.096. Epub 2005 Sep 8. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16150465
-
Intra- and extracellular regulation of activity and processing of legumain by cystatin E/M.Biochimie. 2012 Dec;94(12):2590-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.07.026. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Biochimie. 2012. PMID: 22902879
-
The biology of cystatin M/E and its cognate target proteases.J Invest Dermatol. 2009 Jun;129(6):1327-38. doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.40. Epub 2009 Mar 5. J Invest Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19262604 Review.
-
Cystatin M/E (Cystatin 6): A Janus-Faced Cysteine Protease Inhibitor with Both Tumor-Suppressing and Tumor-Promoting Functions.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 14;13(8):1877. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081877. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Counter Selection Substrate Library Strategy for Developing Specific Protease Substrates and Probes.Cell Chem Biol. 2016 Aug 18;23(8):1023-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.05.020. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Cell Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27478158 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolysis mediated by cysteine cathepsins and legumain-recent advances and cell biological challenges.Protoplasma. 2015 May;252(3):755-74. doi: 10.1007/s00709-014-0730-0. Epub 2014 Nov 16. Protoplasma. 2015. PMID: 25398648 Review.
-
Knockdown of Legumain Suppresses Cervical Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion.Oncol Res. 2016 Jan 21;23(1-2):7-12. doi: 10.3727/096504015X14410238486649. Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 26802645 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathologic significance of legumain overexpression in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 26;5:16599. doi: 10.1038/srep16599. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26607955 Free PMC article.
-
A multifunctional protease inhibitor to regulate endolysosomal function.ACS Chem Biol. 2011 Nov 18;6(11):1198-204. doi: 10.1021/cb200292c. Epub 2011 Sep 19. ACS Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21910425 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

