Endogenous leptin signaling in the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius and area postrema is required for energy balance regulation
- PMID: 20074530
- PMCID: PMC2807619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.10.009
Endogenous leptin signaling in the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius and area postrema is required for energy balance regulation
Erratum in
-
Endogenous Leptin Signaling in the Caudal Nucleus Tractus Solitarius and Area Postrema Is Required for Energy Balance Regulation.Cell Metab. 2016 Apr 12;23(4):744. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.02.009. Cell Metab. 2016. PMID: 27076082 No abstract available.
Abstract
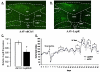
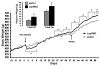
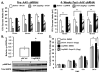
Medial nucleus tractus solitarius (mNTS) neurons express leptin receptors (LepRs), and intra-mNTS delivery of leptin reduces food intake and body weight. Here, the contribution of endogenous LepR signaling in mNTS neurons to energy balance control was examined. Knockdown of LepR in mNTS and area postrema (AP) neurons of rats (LepRKD) via adeno-associated virus short hairpin RNA-interference (AAV-shRNAi) resulted in significant hyperphagia for chow, high-fat, and sucrose diets, yielding increased body weight and adiposity. The chronic hyperphagia of mNTS/AP LepRKD rats is likely mediated by a reduction in leptin potentiation of gastrointestinal satiation signaling, as LepRKD rats showed decreased sensitivity to the intake-reducing effects of cholecystokinin. LepRKD rats showed increased basal AMP-kinase activity in mNTS/AP micropunches, and pharmacological data suggest that this increase provides a likely mechanism for their chronic hyperphagia. Overall these findings demonstrate that LepRs in mNTS and AP neurons are required for normal energy balance control.
2010 Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bamshad M, Aoki VT, Adkison MG, Warren WS, Bartness TJ. Central nervous system origins of the sympathetic nervous system outflow to white adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:R291–299. - PubMed
-
- Barsh GS, Schwartz MW. Genetic approaches to studying energy balance: perception and integration. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:589–600. - PubMed
-
- Bence KK, Delibegovic M, Xue B, Gorgun CZ, Hotamisligil GS, Neel BG, Kahn BB. Neuronal PTP1B regulates body weight, adiposity and leptin action. Nat Med. 2006;12:917–924. - PubMed
-
- Blevins JE, Schwartz MW, Baskin DG. Evidence that paraventricular nucleus oxytocin neurons link hypothalamic leptin action to caudal brain stem nuclei controlling meal size. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004;287:R87–96. - PubMed
-
- Bowers RR, Festuccia WT, Song CK, Shi H, Migliorini RH, Bartness TJ. Sympathetic innervation of white adipose tissue and its regulation of fat cell number. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004;286:R1167–1175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

