Differential IL-7 responses in developing human thymocytes
- PMID: 20074604
- PMCID: PMC2896073
- DOI: 10.1016/j.humimm.2010.01.009
Differential IL-7 responses in developing human thymocytes
Abstract
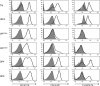
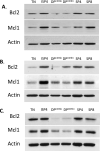
Interleukin (IL)-7 is a factor essential for mouse and human thymopoiesis. Mouse thymocytes have altered sensitivities to IL-7 at different developmental stages. CD4/CD8 double positive (DP) mouse thymocytes are shielded from the influence of IL-7 because of loss of CD127 (IL-7Ralpha). In this study, we assessed IL-7 receptor expression and IL-7 signaling in human thymocytes. We found human DP cells to be severely limited in their ability to phosphorylate STAT-5 in response to IL-7. The relative expression levels of the IL-7-inducible proteins Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 were also lower in human DP cells, consistent with a stage-specific decrease in IL-7 responsiveness. IL-7 responses were restored in a subset of cells that matured past the DP stage. Unlike the regulation of IL-7 signaling in mouse thymocytes, loss of IL-7 signaling in human DP cells was not due to absence of CD127, but instead correlated with downregulation of CD132 (common gamma chain).
.
Figures

References
-
- Dik WA, Pike-Overzet K, Weerkamp F, de Ridder D, de Haas EF, Baert MR, van der Spek P, Koster EE, Reinders MJ, van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Staal FJ. New insights on human T cell development by quantitative T cell receptor gene rearrangement studies and gene expression profiling. J Exp Med. 2005;201(11):1715. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fehling HJ, von Boehmer H. Early alpha beta T cell development in the thymus of normal and genetically altered mice. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9(2):263. - PubMed
-
- Spits H. Development of alphabeta T cells in the human thymus. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(10):760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

