Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 induces alpha-synuclein expression via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway
- PMID: 20074637
- PMCID: PMC3163153
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.01.006
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 induces alpha-synuclein expression via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway
Abstract
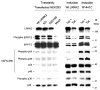
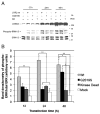
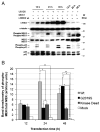
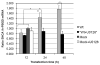
Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are the most frequent cause of autosomal-dominant Parkinson's disease (PD). The second known autosomal-dominant PD gene (SNCA) encodes alpha-synuclein, which is deposited in Lewy bodies, the neuropathological hallmark of PD. LRRK2 contains a kinase domain with homology to mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases (MAPKKKs) and its activity has been suggested to be a key factor in LRRK2-associated PD. Here we investigated the role of LRRK2 in signal transduction pathways to identify putative PD-relevant downstream targets. Over-expression of wild-type [wt]LRRK2 in human embryonic kidney HEK293 cells selectively activated the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) module. PD-associated mutants G2019S and R1441C, but not kinase-dead LRRK2, induced ERK phosphorylation to the same extent as [wt]LRRK2, indicating that this effect is kinase-dependent. However, ERK activation by mutant R1441C and G2019S was significantly slower than that for [wt]LRRK2, despite similar levels of expression. Furthermore, induction of the ERK module by LRRK2 was associated to a small but significant induction of SNCA, which was suppressed by treatment with the selective MAPK/ERK kinase inhibitor U0126. This pathway linking the two dominant PD genes LRRK2 and SNCA may offer an interesting target for drug therapy in both familial and sporadic disease.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
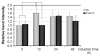

Similar articles
-
Age-dependent accumulation of oligomeric SNCA/α-synuclein from impaired degradation in mutant LRRK2 knockin mouse model of Parkinson disease: role for therapeutic activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA).Autophagy. 2020 Feb;16(2):347-370. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1603545. Epub 2019 Apr 14. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 30983487 Free PMC article.
-
Lrrk2 phosphorylates alpha synuclein at serine 129: Parkinson disease implications.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Sep 11;387(1):149-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.06.142. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19576176
-
Adenoviral-mediated expression of G2019S LRRK2 induces striatal pathology in a kinase-dependent manner in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 May;77:49-61. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.02.019. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25731749
-
α-Synuclein, leucine-rich repeat kinase-2, and manganese in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease.Neurotoxicology. 2011 Oct;32(5):622-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2011.01.003. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Neurotoxicology. 2011. PMID: 21238487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERKed by LRRK2: a cell biological perspective on hereditary and sporadic Parkinson's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1842(8):1273-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.11.005. Epub 2013 Nov 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24225420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dictyostelium discoideum as a Model for Investigating Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Oct 27;15:759532. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.759532. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34776869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-335 Targets LRRK2 and Mitigates Inflammation in Parkinson's Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 15;9:661461. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.661461. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34211970 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: pathogenesis and neuroprotection.Parkinsons Dis. 2010 Dec 26;2011:617472. doi: 10.4061/2011/617472. Parkinsons Dis. 2010. PMID: 21234411 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between SNCA, LRRK2 and GAK increases susceptibility to Parkinson's disease in a Chinese population.eNeurologicalSci. 2015 Aug 7;1(1):3-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2015.08.001. eCollection 2015 Mar. eNeurologicalSci. 2015. PMID: 29479569 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of the Nrf2/Bach1 Signaling Pathway in Parkinson's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 9;11(9):1780. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091780. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139853 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dauer W, Przedborski S. Neuron. 2003;39(6):889–909. - PubMed
-
- Goedert M. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2(7):492–501. - PubMed
-
- Biskup S, Gerlach M, Kupsch A, Reichmann H, Riederer P, Vieregge P, Wullner U, Gasser T. J Neurol. 2008;255(Suppl 5):8–17. - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassia-dou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M. Nature. 1997;388(6645):839–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

