T-cell antagonism by short half-life pMHC ligands can be mediated by an efficient trapping of T-cell polarization toward the APC
- PMID: 20075022
- PMCID: PMC2806700
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911258107
T-cell antagonism by short half-life pMHC ligands can be mediated by an efficient trapping of T-cell polarization toward the APC
Abstract
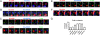
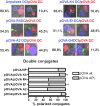
T-cell activation results from productive T-cell receptor (TCR) engagement by a cognate peptide-MHC (pMHC) complex on the antigen presenting cell (APC) surface, a process leading to the polarization of the T-cell secretory machinery toward the APC interface. We have previously shown that the half-life of the TCR/pMHC interaction and the density of pMHC on the APC are two parameters determining T-cell activation. However, whether the half-life of the TCR/pMHC interaction can modulate the efficiency of T-cell secretory machinery polarization toward an APC still remains unclear. Here, by using altered peptide ligands conferring different half-lives to the TCR/pMHC interaction, we have tested how this parameter can control T-cell polarization. We observed that only TCR/pMHC interactions with intermediate half-lives can promote the assembly of synapses that lead to T-cell activation. Strikingly, intermediate half-life interactions can be competed out by short half-life interactions, which can efficiently promote T-cell polarization and antagonize T-cell activation that was induced by activating intermediate half-life interactions. However, short TCR/pMHC interactions fail at promoting phosphorylation of signaling molecules at the T-cell-APC contact interface, which are needed for T-cell activation. Our data suggest that although intermediate half-life pMHC ligands promote assembly of activating synapses, this process can be inhibited by short half-life antagonistic pMHC ligands, which promote the assembly of non activating synapses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
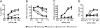
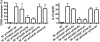

References
-
- Carreño LJ, González PA, Kalergis AM. Modulation of T cell function by TCR/pMHC binding kinetics. Immunobiology. 2006;211:47–64. - PubMed
-
- Kalergis AM. Modulation of T cell immunity by TCR/pMHC dwell time and activating/inhibitory receptor pairs on the antigen-presenting cell. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:233–244. - PubMed
-
- González PA, Carreño LJ, Figueroa CA, Kalergis AM. Modulation of immunological synapse by membrane-bound and soluble ligands. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007;18:19–31. - PubMed
-
- Grakoui A, et al. The immunological synapse: A molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science. 1999;285:221–227. - PubMed
-
- Huppa JB, Davis MM. T-cell-antigen recognition and the immunological synapse. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:973–983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

