CD36 is a novel serum amyloid A (SAA) receptor mediating SAA binding and SAA-induced signaling in human and rodent cells
- PMID: 20075072
- PMCID: PMC2832998
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007526
CD36 is a novel serum amyloid A (SAA) receptor mediating SAA binding and SAA-induced signaling in human and rodent cells
Abstract
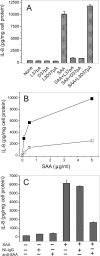
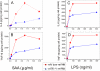
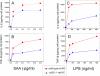
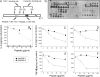
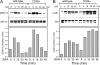
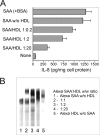
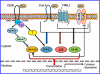
Serum amyloid A (SAA) is a major acute phase protein involved in multiple physiological and pathological processes. This study provides experimental evidence that CD36, a phagocyte class B scavenger receptor, functions as a novel SAA receptor mediating SAA proinflammatory activity. The uptake of Alexa Fluor 488 SAA as well as of other well established CD36 ligands was increased 5-10-fold in HeLa cells stably transfected with CD36 when compared with mock-transfected cells. Unlike other apolipoproteins that bind to CD36, only SAA induced a 10-50-fold increase of interleukin-8 secretion in CD36-overexpressing HEK293 cells when compared with control cells. SAA-mediated effects were thermolabile, inhibitable by anti-SAA antibody, and also neutralized by association with high density lipoprotein but not by association with bovine serum albumin. SAA-induced cell activation was inhibited by a CD36 peptide based on the CD36 hexarelin-binding site but not by a peptide based on the thrombospondin-1-binding site. A pronounced reduction (up to 60-75%) of SAA-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion was observed in cd36(-/-) rat macrophages and Kupffer cells when compared with wild type rat cells. The results of the MAPK phosphorylation assay as well as of the studies with NF-kappaB and MAPK inhibitors revealed that two MAPKs, JNK and to a lesser extent ERK1/2, primarily contribute to elevated cytokine production in CD36-overexpressing HEK293 cells. In macrophages, four signaling pathways involving NF-kappaB and three MAPKs all appeared to contribute to SAA-induced cytokine release. These observations indicate that CD36 is a receptor mediating SAA binding and SAA-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion predominantly through JNK- and ERK1/2-mediated signaling.
Figures
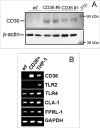
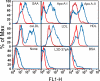
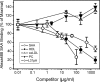
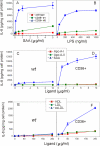

References
-
- Kushner I., Rzewnicki D. L. (1994) Baillieres Clin. Rheumatol. 8, 513–530 - PubMed
-
- Kushner I. (1982) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 389, 39–48 - PubMed
-
- Uhlar C. M., Whitehead A. S. (1999) Eur. J. Biochem. 265, 501–523 - PubMed
-
- Malle E., Steinmetz A., Raynes J. G. (1993) Atherosclerosis 102, 131–146 - PubMed
-
- Patel H., Fellowes R., Coade S., Woo P. (1998) Scand. J. Immunol. 48, 410–418 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

