The ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of leukemia and multiple myeloma
- PMID: 20075161
- PMCID: PMC2920204
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-231191
The ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of leukemia and multiple myeloma
Abstract
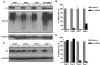
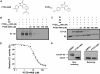
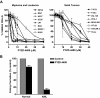
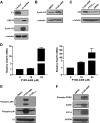
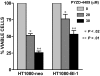
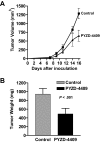
The proteasomal pathway of protein degradation involves 2 discrete steps: ubiquitination and degradation. Here, we evaluated the effects of inhibiting the ubiquitination pathway at the level of the ubiquitin-activating enzyme UBA1 (E1). By immunoblotting, leukemia cell lines and primary patient samples had increased protein ubiquitination. Therefore, we examined the effects of genetic and chemical inhibition of the E1 enzyme. Knockdown of E1 decreased the abundance of ubiquitinated proteins in leukemia and myeloma cells and induced cell death. To further investigate effects of E1 inhibition in malignancy, we discovered a novel small molecule inhibitor, 3,5-dioxopyrazolidine compound, 1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-4-[(5-nitro-2-furyl)methylene]-3,5-pyrazolidinedione (PYZD-4409). PYZD-4409 induced cell death in malignant cells and preferentially inhibited the clonogenic growth of primary acute myeloid leukemia cells compared with normal hematopoietic cells. Mechanistically, genetic or chemical inhibition of E1 increased expression of E1 stress markers. Moreover, BI-1 overexpression blocked cell death after E1 inhibition, suggesting ER stress is functionally important for cell death after E1 inhibition. Finally, in a mouse model of leukemia, intraperitoneal administration of PYZD-4409 decreased tumor weight and volume compared with control without untoward toxicity. Thus, our work highlights the E1 enzyme as a novel target for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel ubiquitin-activating enzyme inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 Sep 1;28(16):2723-2727. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 3. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 29548576
-
Preclinical evaluation of the selective small-molecule UBA1 inhibitor, TAK-243, in acute myeloid leukemia.Leukemia. 2019 Jan;33(1):37-51. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0167-0. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Leukemia. 2019. PMID: 29884901
-
Novel p97/VCP inhibitor induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in both bortezomib-sensitive and -resistant multiple myeloma cells.Cancer Sci. 2019 Oct;110(10):3275-3287. doi: 10.1111/cas.14154. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31368616 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the ubiquitin E1 as a novel anti-cancer strategy.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(18):3201-9. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319180004. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23151135 Review.
-
[The role of different E3 ubiquitin ligases in regulation of the P53 tumor suppressor protein].Tsitologiia. 2013;55(10):673-87. Tsitologiia. 2013. PMID: 25509121 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Inhibiting the protein ubiquitination cascade by ubiquitin-mimicking short peptides.Org Lett. 2012 Nov 16;14(22):5760-3. doi: 10.1021/ol3027736. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Org Lett. 2012. PMID: 23134251 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the Mitochondrial Protease ClpP as a Therapeutic Strategy for Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Cancer Cell. 2015 Jun 8;27(6):864-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.05.004. Cancer Cell. 2015. PMID: 26058080 Free PMC article.
-
Mode of inhibitory binding of epigallocatechin gallate to the ubiquitin-activating enzyme Uba1 via accelerated molecular dynamics.RSC Adv. 2021 Feb 22;11(14):8264-8276. doi: 10.1039/d0ra09847g. eCollection 2021 Feb 17. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35423322 Free PMC article.
-
Monoubiquitination of Cancer Stem Cell Marker CD133 at Lysine 848 Regulates Its Secretion and Promotes Cell Migration.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Jul 16;38(15):e00024-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00024-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29760280 Free PMC article.
-
The non-canonical ubiquitin activating enzyme UBA6 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of mammary epithelial cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 15;8(50):87480-87493. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20900. eCollection 2017 Oct 20. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29152096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher RI, Bernstein SH, Kahl BS, et al. Multicenter phase II study of bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(30):4867–4874. - PubMed
-
- Richardson PG, Sonneveld P, Schuster MW, et al. Bortezomib or high-dose dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(24):2487–2498. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation and some of its roles in the control of the cell division cycle. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12(9):1191–1197. - PubMed
-
- Burger AM, Seth AK. The ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation pathway in cancer: therapeutic implications. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40(15):2217–2229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

