Rapid genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms influencing warfarin drug response by surface-enhanced laser desorption and ionization time-of-flight (SELDI-TOF) mass spectrometry
- PMID: 20075209
- PMCID: PMC2871722
- DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2010.090084
Rapid genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms influencing warfarin drug response by surface-enhanced laser desorption and ionization time-of-flight (SELDI-TOF) mass spectrometry
Abstract
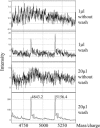
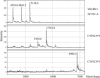
Warfarin exhibits significant interindividual variability in dosing requirements. Different drug responses are partly attributed to the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that influence either drug action or drug metabolism. Rapid genotyping of these SNPs helps clinicians to choose appropriate initial doses to quickly achieve anticoagulation effects and to prevent complications. We report a novel application of surface-enhanced laser desorption and ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SELDI-TOF MS) in the rapid genotyping of SNPs that impact warfarin efficacy. The SNPs were first amplified by PCR and then underwent single base extension to generate the specific SNP product. Next, genetic variants displaying different masses were bound to Q10 anionic proteinChips and then genotyped by using SELDI-TOF MS in a multiplex fashion. SELDI-TOF MS offered unique properties of on-chip sample enrichment and clean-ups, which streamlined the testing procedures and eliminated many tedious experimental steps required by the conventional MS-based method. The turn-around time for genotyping three known warfarin-related SNPs, CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3, and VKORC1 3673G>A by SELDI-TOF MS was less than 5 hours. The analytical accuracy of this method was confirmed both by bidirectional DNA sequencing and by comparing the genotype results (n = 189) obtained by SELDI-TOF MS to reports from a clinical reference laboratory. This new multiplex genotyping method provides an excellent clinical laboratory platform to promote personalized medicine in warfarin therapy.
Figures
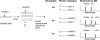

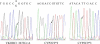

Similar articles
-
Rapid multiplexed genotyping for hereditary thrombophilia by SELDI-TOF mass spectrometry.Diagn Mol Pathol. 2010 Mar;19(1):54-61. doi: 10.1097/PDM.0b013e3181a814bf. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20186013
-
Multiplex genotyping of CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 SNPs using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.Pharmacogenomics. 2010 Apr;11(4):559-71. doi: 10.2217/pgs.09.172. Pharmacogenomics. 2010. PMID: 20350138
-
Multiplex genotyping of cytochrome p450 single-nucleotide polymorphisms by use of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.Clin Chem. 2007 May;53(5):933-9. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2006.080739. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Clin Chem. 2007. PMID: 17384008
-
The pharmocogenomics of warfarin: closing in on personalized medicine.Mol Interv. 2006 Aug;6(4):223-7. doi: 10.1124/mi.6.4.8. Mol Interv. 2006. PMID: 16960144 Review.
-
Use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for multiplex genotyping.Adv Clin Chem. 2011;53:1-29. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-385855-9.00001-1. Adv Clin Chem. 2011. PMID: 21404912 Review.
References
-
- Kim S, Misra A. SNP genotyping: technologies and biomedical applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2007;9:289–320. - PubMed
-
- Tost J, Gut IG. Genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms by MALDI mass spectrometry in clinical applications. Clin Biochem. 2005;38:335–350. - PubMed
-
- Humeny A, Bonk T, Berkholz A, Wildt L, Becker CM. Genotyping of thrombotic risk factors by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Clin Biochem. 2001;34:531–536. - PubMed
-
- Hung K, Sun X, Ding H, Kalafatis M, Simioni P, Guo B. A matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight based method for screening the 1691G–> A mutation in the factor V gene. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2002;13:117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

