How the noninflammasome NLRs function in the innate immune system
- PMID: 20075243
- PMCID: PMC3943909
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1184004
How the noninflammasome NLRs function in the innate immune system
Abstract
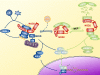
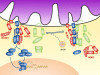
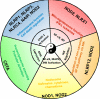
NLR (nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat-containing) proteins have rapidly emerged as central regulators of immunity and inflammation with demonstrated relevance to human diseases. Much attention has focused on the ability of several NLRs to activate the inflammasome complex and drive proteolytic processing of inflammatory cytokines; however, NLRs also regulate important inflammasome-independent functions in the immune system. We discuss several of these functions, including the regulation of canonical and noncanonical NF-kappaB activation, mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, cytokine and chemokine production, antimicrobial reactive oxygen species production, type I interferon production, and ribonuclease L activity. We also explore the mechanistic basis of these functions and describe current challenges in the field.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI057157/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK38108/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DE016326/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- AI063031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI077437/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK038108/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057157/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI088255/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA131645/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA131645/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI031496/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI031496/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI077437/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI029564/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE016326/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

