Regulation of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system
- PMID: 20075244
- PMCID: PMC3645875
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1183021
Regulation of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system
Abstract
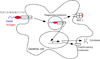
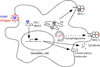
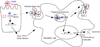
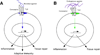
Twenty years after the proposal that pattern recognition receptors detect invasion by microbial pathogens, the field of immunology has witnessed several discoveries that have elucidated receptors and signaling pathways of microbial recognition systems and how they control the generation of T and B lymphocyte-mediated immune responses. However, there are still many fundamental questions that remain poorly understood, even though sometimes the answers are assumed to be known. Here, we discuss some of these questions, including the mechanisms by which pathogen-specific innate immune recognition activates antigen-specific adaptive immune responses and the roles of different types of innate immune recognition in host defense from infection and injury.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21AI083242/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI054359/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 AI081884/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI046688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI064705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071754/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI083242/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI064705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK071754/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37AI046688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI055502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI055502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI054359/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057160/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

