Combination of NEP 1-40 treatment and motor training enhances behavioral recovery after a focal cortical infarct in rats
- PMID: 20075346
- PMCID: PMC2853474
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.572073
Combination of NEP 1-40 treatment and motor training enhances behavioral recovery after a focal cortical infarct in rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Although myelin-associated neurite outgrowth disinhibitors have shown promise in restoring motor function after stroke, their interactive effects with motor training have rarely been investigated. The present study examined whether a combinatorial treatment (NEP 1-40+motor rehabilitation) is more effective than either treatment alone in promoting motor recovery after focal ischemic injury.
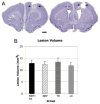
Methods: Adult rats were assigned to one of 3 treatment groups (infarct/NEP 1-40+motor training, infarct/NEP 1-40 only, infarct/motor training only) and 2 control groups (infarct/no treatment, intact/no treatment). A focal ischemic infarct was induced by microinjecting endothelin-1 into the motor cortex. Therapeutic treatments were initiated 1 week postinfarct and included intraventricular infusion of the pharmacological agent NEP 1-40 and motor training (skilled reach task). Behavioral assessments on skilled reach, foot fault, and cylinder tests were conducted before the infarct and for 5 weeks postinfarct.
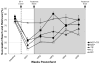
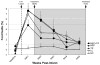
Results: Rats demonstrated significant forelimb impairment on skilled reach and foot fault tests after the infarct. Although all infarct groups improved over time, motor training alone and NEP 1-40 alone facilitated recovery on the skilled reach task at the end of treatment Weeks 2 and 4, respectively. However, only NEP 1-40 paired with motor training facilitated recovery after 1 week of treatment in addition to treatment at Weeks 2 and 4. Finally, only the NEP 1-40+motor training group maintained a performance level equivalent to that of the intact group over the entire period of posttreatment assessment.
Conclusions: This study suggests that behavioral training interacts with the effects of the axonal growth promoter, NEP 1-40, and may accelerate behavioral recovery after focal cortical ischemia.
Figures

References
-
- Kleim JA, Barbay S, Cooper NR, Hogg TM, Reidel CN, Remple MS, Nudo RJ. Motor learning-dependent synaptogenesis is localized to functionally reorganized motor cortex. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002;77:63–77. - PubMed
-
- Nudo RJ. Postinfarct cortical plasticity and behavioral recovery. Stroke. 2007;38:840–845. - PubMed
-
- Cramer SC, Riley JD. Neuroplasticity and brain repair after stroke. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008;21:76–82. - PubMed
-
- Wolf SL, Winstein CJ, Miller JP, Taub E, Uswatte G, Morris D, Giuliani C, Light KE, Nichols-Larsen D. Effect of constraint-induced movement therapy on upper extremity function 3 to 9 months after stroke: the EXCITE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2006;296:2095–2104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

