Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20075733
- PMCID: PMC3121048
- DOI: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e328336474d
Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Purpose of review: To review the recently discovered genetic risk loci in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the pathways they implicate, and the genetic architecture of RA.
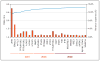
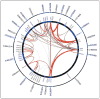
Recent findings: Since 2008 investigators have identified many common genetic variants that confer disease risk through single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping studies; the list of variants will no doubt continue to expand at a rapid rate as genotyping technologies evolve and case-control sample collections continue to grow. In aggregate, these variants implicate pathways leading to NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) activation, the interluekin-2 signaling pathway, and T-cell activation.
Summary: Although the effect of any individual variant is modest and even in aggregate considerably less than that of the major histocompatability complex, discovery of recent risk variants suggests immunological processes that are involved in disease pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Isenberg D. Oxford textbook of rheumatology. 3. Oxford: New York: Oxford University Press; 2004.
-
- Heberden W. Commentaries on the history and cure of diseases. 3. London: Printed for T. Payne; 1806.
-
- Gregersen PK, Silver J, Winchester RJ. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987;30:1205–1213. - PubMed
-
- Stastny P. Association of the B-cell alloantigen DRw4 with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978;298:869–871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

