DNA diagnostics: nanotechnology-enhanced electrochemical detection of nucleic acids
- PMID: 20075759
- PMCID: PMC2876983
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181d361c3
DNA diagnostics: nanotechnology-enhanced electrochemical detection of nucleic acids
Abstract
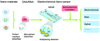
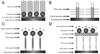
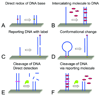
The detection of mismatched base pairs in DNA plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of genetic-related diseases and conditions, especially for early stage treatment. Among the various biosensors that have been used for DNA detection, EC sensors show great promise because they are capable of precise DNA recognition and efficient signal transduction. Advancements in micro- and nanotechnologies, specifically fabrication techniques and new nanomaterials, have enabled for the development of highly sensitive, highly specific sensors making them attractive for the detection of small sequence variations. Furthermore, the integration of sensors with sample preparation and fluidic processes enables for rapid, multiplexed DNA detection essential for POC clinical diagnostics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nanotechnology-Enhanced No-Wash Biosensors for in Vitro Diagnostics of Cancer.ACS Nano. 2017 Jun 27;11(6):5238-5292. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b02618. Epub 2017 Jun 14. ACS Nano. 2017. PMID: 28590117 Review.
-
Point-of-care nucleic acid detection using nanotechnology.Nanoscale. 2013 Nov 7;5(21):10141-54. doi: 10.1039/c3nr04015a. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Nanoscale. 2013. PMID: 24057263 Review.
-
A review of point-of-care (POC) and lab-on-chip (LOC) approaches in molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for biomedical applications.Anal Chim Acta. 2025 Jul 1;1357:344080. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2025.344080. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Anal Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40316385 Review.
-
Carbon nanostructures as immobilization platform for DNA: A review on current progress in electrochemical DNA sensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 Nov 15;97:226-237. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.06.001. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 28601788 Review.
-
CRISPR-based electrochemical biosensors: an alternative for point-of-care diagnostics?Talanta. 2024 Oct 1;278:126467. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.126467. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Talanta. 2024. PMID: 38968657 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleic Acid-Based Sensing Techniques for Diagnostics and Surveillance of Influenza.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 12;11(2):47. doi: 10.3390/bios11020047. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostics Strategies with Electrochemical Affinity Biosensors Using Carbon Nanomaterials as Electrode Modifiers.Diagnostics (Basel). 2016 Dec 26;7(1):2. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics7010002. Diagnostics (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28035946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fighting COVID-19: Integrated Micro- and Nanosystems for Viral Infection Diagnostics.Matter. 2020 Sep 2;3(3):628-651. doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2020.06.015. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Matter. 2020. PMID: 32838297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An ion-exchange nanomembrane sensor for detection of nucleic acids using a surface charge inversion phenomenon.Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Oct 15;60:92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.008. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014. PMID: 24787123 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and application of a real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification system for the detection of CYP2C19 polymorphisms.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 1;6:26533. doi: 10.1038/srep26533. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27246657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaud AL, Belmont JW, et al. Array-based DNA diagnostics: Let the revolution begin. Annu Rev Med. 2008;59:113–129. - PubMed
-
- Roberts DG, Morrison TB, Liu-Cordero SN, Cho J, Garcia J, Kanigan TS, Munnelly K, Brenan CJ. A nanoliter fluidic platform for large-scale single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping. Biotechniques. 2009;46:IX–XIII. - PubMed
-
- Tost J, Gut IG. Genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms by MALDI mass spectrometry in clinical applications. Clin Biochem. 2005;38:335–350. - PubMed
-
- Murphy KM, Berg KD. Mutation and single nucleotide polymorphism detection using temperature gradient capillary electrophoresis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003;3:811–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

