Nucleolar retention of a translational C/EBPalpha isoform stimulates rDNA transcription and cell size
- PMID: 20075868
- PMCID: PMC2810377
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.404
Nucleolar retention of a translational C/EBPalpha isoform stimulates rDNA transcription and cell size
Abstract
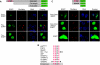
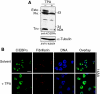
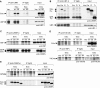
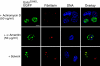
The messenger RNA of the intronless CEBPA gene is translated into distinct protein isoforms through the usage of consecutive translation initiation sites. These translational isoforms have distinct functions in the regulation of differentiation and proliferation due to the presence of different N-terminal sequences. Here, we describe the function of an N-terminally extended protein isoform of CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) that is translated from an alternative non-AUG initiation codon. We show that a basic amino-acid motif within its N-terminus is required for nucleolar retention and for interaction with nucleophosmin (NPM). In the nucleoli, extended-C/EBPalpha occupies the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) promoter and associates with the Pol I-specific factors upstream-binding factor 1 (UBF-1) and SL1 to stimulate rRNA synthesis. Furthermore, during differentiation of HL-60 cells, endogenous expression of extended-C/EBPalpha is lost concomitantly with nucleolar C/EBPalpha immunostaining probably reflecting the reduced requirement for ribosome biogenesis in differentiated cells. Finally, overexpression of extended-C/EBPalpha induces an increase in cell size. Altogether, our results suggest that control of rRNA synthesis is a novel function of C/EBPalpha adding to its role as key regulator of cell growth and proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Arabi A, Wu S, Ridderstrale K, Bierhoff H, Shiue C, Fatyol K, Fahlen S, Hydbring P, Soderberg O, Grummt I, Larsson LG, Wright AP (2005) c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat Cell Biol 7: 303–310 - PubMed
-
- Bararia D, Trivedi AK, Zada AA, Greif PA, Mulaw MA, Christopeit M, Hiddemann W, Bohlander SK, Behre G (2008) Proteomic identification of the MYST domain histone acetyltransferase TIP60 (HTATIP) as a co-activator of the myeloid transcription factor C/EBPalpha. Leukemia 22: 800–807 - PubMed
-
- Baserga R (2007) Is cell size important? Cell Cycle 6: 814–816 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

