An allosteric mechanism of Rho-dependent transcription termination
- PMID: 20075920
- PMCID: PMC2929367
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08669
An allosteric mechanism of Rho-dependent transcription termination
Erratum in
- Nature. 2010 Aug 19;466(7309):1006
Abstract
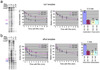
Rho is the essential RNA helicase that sets the borders between transcription units and adjusts transcriptional yield to translational needs in bacteria. Although Rho was the first termination factor to be discovered, the actual mechanism by which it reaches and disrupts the elongation complex (EC) is unknown. Here we show that the termination-committed Rho molecule associates with RNA polymerase (RNAP) throughout the transcription cycle; that is, it does not require the nascent transcript for initial binding. Moreover, the formation of the RNAP-Rho complex is crucial for termination. We show further that Rho-dependent termination is a two-step process that involves rapid EC inactivation (trap) and a relatively slow dissociation. Inactivation is the critical rate-limiting step that establishes the position of the termination site. The trap mechanism depends on the allosterically induced rearrangement of the RNAP catalytic centre by means of the evolutionarily conserved mobile trigger-loop domain, which is also required for EC dissociation. The key structural and functional similarities, which we found between Rho-dependent and intrinsic (Rho-independent) termination pathways, argue that the allosteric mechanism of termination is general and likely to be preserved for all cellular RNAPs throughout evolution.
Figures


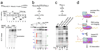
References
-
- Adhya S, Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. - PubMed
-
- Richardson JP. Preventing the synthesis of unused transcripts by Rho factor. Cell. 1991;64:1047–1049. - PubMed
-
- Roberts JW. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969;224:1168–1174. - PubMed
-
- Geiselmann J, Yager TD, Gill SC, Calmettes P, von Hippel PH. Physical properties of the Escherichia coli transcription termination factor Rho. 1. Association states and geometry of the Rho hexamer. Biochemistry. 1992;31:111–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

