Aggressive glucose control for acute ischemic stroke patients by insulin infusion
- PMID: 20076797
- PMCID: PMC2806538
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2009.5.4.167
Aggressive glucose control for acute ischemic stroke patients by insulin infusion
Abstract
Background and purpose: Hyperglycemia after acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is associated with poor outcomes. However, there is no consensus as to the optimal method for glycemic control. We designed an insulin infusion protocol for aggressive glucose control and investigated its efficacy and safety.
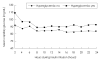
Methods: We applied our protocol to patients within 48 hours after AIS or transient ischemic attack (TIA) with an initial capillary glucose level of between 100 and 399 mg/dL (5.6-22.2 mmol/L). An insulin solution comprising 40 or 50 U of human regular insulin in 500 mL of 5% dextrose was administered for 24 hours. Capillary glucose was measured every 2 hours and the infusion rate was adjusted according to a nomogram with a target range of 80-129 mg/dL (4.4-7.2 mmol/L). Changes in glucose and overall glucose levels during insulin infusion were analyzed according to the presence of diabetes or admission hyperglycemia (admission glucose >139 mg/dL or 7.7 mmol/L) by the generalized estimating equation method.
Results: The study cohort comprised 115 consecutive patients. Glucose was significantly lowered from 160+/-57 mg/dL (8.9+/-3.2 mmol/L) at admission to 93+/-28 mg/dL (5.2+/-1.6 mmol/L) during insulin infusion (p<0.05). Laboratory hypoglycemia (capillary glucose <80 mg/dL or 4.4 mmol/L) occurred in 91 (71%) patients, 11 (10%) of whom had symptomatic hypoglycemia. Although glucose levels were significantly lowered and maintained within the target range in all patients, overall glucose levels were significantly higher in patients with diabetes or hyperglycemia (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Our insulin-infusion protocol was effective in glycemic control for patients with AIS or TIA. Further modification is needed to improve the efficacy and safety of this procedure, and tailored intervention should be considered according to glycemic status.
Keywords: hyperglycemia; insulin; ischemic stroke.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intravenous insulin therapy in the maintenance of strict glycemic control in nondiabetic acute stroke patients with mild hyperglycemia.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011 Mar-Apr;20(2):150-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2009.11.013. Epub 2010 Jul 10. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011. PMID: 20621520 Clinical Trial.
-
Software-guided insulin dosing improves intrapartum glycemic management in women with diabetes mellitus.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Aug;219(2):191.e1-191.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 May 8. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29750952
-
Treatment of hyperglycemia in ischemic stroke (THIS): a randomized pilot trial.Stroke. 2008 Feb;39(2):384-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.493544. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Stroke. 2008. PMID: 18096840 Clinical Trial.
-
Addressing hyperglycemia from hospital admission to discharge.Curr Med Res Opin. 2010 Mar;26(3):589-98. doi: 10.1185/03007990903566822. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010. PMID: 20078323 Review.
-
Guidelines for the use of an insulin infusion for the management of hyperglycemia in critically ill patients.Crit Care Med. 2012 Dec;40(12):3251-76. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182653269. Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 23164767 Review.
Cited by
-
Treating hyperglycemia in neurocritical patients: benefits and perils.Neurocrit Care. 2010 Dec;13(3):425-38. doi: 10.1007/s12028-010-9404-8. Neurocrit Care. 2010. PMID: 20652767 Review.
-
Managing post stroke hyperglycaemia: moderate glycaemic control is better? An update.EXCLI J. 2014 Aug 13;13:825-33. eCollection 2014. EXCLI J. 2014. PMID: 26417305 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Capes SE, Hunt D, Malmberg K, Pathak P, Gerstein HC. Stress hyperglycemia and prognosis of stroke in nondiabetic and diabetic patients: a systematic overview. Stroke. 2001;32:2426–2432. - PubMed
-
- Scott JF, Robinson GM, French JM, O'Connell JE, Alberti KG, Gray CS. Prevalence of admission hyperglycaemia across clinical subtypes of acute stroke. Lancet. 1999;353:376–377. - PubMed
-
- Toni D, Sacchetti ML, Argentino C, Gentile M, Cavalletti C, Frontoni M, et al. Does hyperglycaemia play a role on the outcome of acute ischaemic stroke patients? J Neurol. 1992;239:382–386. - PubMed
-
- Quinn TJ, Lees KR. Hyperglycaemia in acute stroke--to treat or not to treat. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;27(Suppl 1):148–155. - PubMed
-
- Allport L, Baird T, Butcher K, Macgregor L, Prosser J, Colman P, et al. Frequency and temporal profile of poststroke hyperglycemia using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1839–1844. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

