In vitro photodynamic therapy with chlorin e6 leads to apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 20077143
- PMCID: PMC2816260
- DOI: 10.1007/s00005-009-0054-5
In vitro photodynamic therapy with chlorin e6 leads to apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
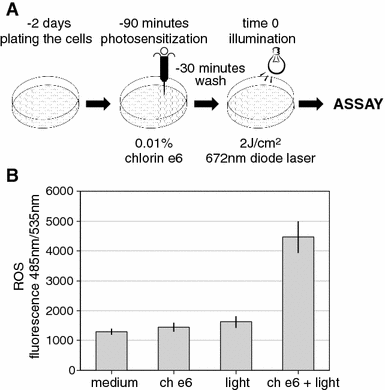
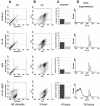
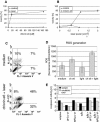
Percutaneous coronary intervention has become the most common and widely implemented method of heart revascularization. However, the development of restenosis remains the major limitation of this method. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) recently emerged as a new and promising method for the prevention of arterial restenosis. Here the efficacy of chlorin e6 in PDT was investigated in vitro using human vascular smooth muscle cells (TG/HA-VSMCs) as one of the cell types crucial in the development of restenosis. PDT-induced cell death was studied on many levels,including annexin V staining, measurement of the generation reactive oxygen species (ROS) and caspase-3 activity,and assessment of changes in mitochondrial membrane potential and fragmentation of DNA. Photosensitization of TG/HA-VSMCs with a 170 lM of chlorin e6 and subsequent illumination with the light of a 672-nm diode laser(2 J/cm2) resulted in the generation of ROS, a decrease in cell membrane polarization, caspase-3 activation, as well as DNA fragmentation. Interestingly, the latter two apoptotic events could not be observed in photosensitized and illuminated NIH3T3 fibroblasts, suggesting different outcomes of the model of PDT in various types of cells. The results obtained with human VSMCs show that chlorin e6 may be useful in the PDT of aerial restenosis, but its efficacy still needs to be established in an animal model.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Photolon™ --photosensitization induces apoptosis via ROS-mediated cross-talk between mitochondria and lysosomes.Int J Oncol. 2011 Oct;39(4):821-31. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1109. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Int J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21725591
-
Efficient preparation of highly pure chlorin e6 and its photodynamic anti-cancer activity in a rat tumor model.Oncol Rep. 2009 Nov;22(5):1085-91. Oncol Rep. 2009. PMID: 19787225
-
Photodynamic therapy with talaporfin sodium induces dose- and time-dependent apoptotic cell death in malignant meningioma HKBMM cells.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2019 Mar;25:29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2018.10.022. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2019. PMID: 30389626
-
Chlorin e6 mediated photodynamic therapy triggers resistance through ATM-related DNA damage response in lung cancer cells.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2022 Mar;37:102645. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102645. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2022. PMID: 34823034
-
Porphyrin-photosensitized processes: their applications in the prevention of arterial restenosis.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2007 Oct;5(4):278-88. doi: 10.2174/187152507782109908. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17979690 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of meta-tetrahydroxyphenylchlorin photodynamic therapy on isogenic colorectal cancer SW480 and SW620 cells with different metastatic potentials.Lasers Med Sci. 2018 Sep;33(7):1581-1590. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2524-7. Epub 2018 May 24. Lasers Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29796953 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorin e6-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle (SPION) Nanoclusters as a Theranostic Agent for Dual-Mode Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 22;9(1):2613. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39036-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30796251 Free PMC article.
-
Photoactive Liposomal Formulation of PVP-Conjugated Chlorin e6 for Photodynamic Reduction of Atherosclerotic Plaque.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 7;20(16):3852. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163852. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31394775 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Mechanism of the c-Myc/NEAT1 Axis Mediating Colorectal Cancer Cell Response to Photodynamic Therapy Treatment.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 28;11:652831. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.652831. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34395239 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Aberrations Associated with Photodynamic Therapy in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 2;20(13):3254. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133254. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31269724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buytaert E, Dewaele M, Agostinis P. Molecular effectors of multiple cell death pathways initiated by photodynamic therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1776:86–107. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Woodburn KW, Shi C, et al. Photodynamic therapy with motexafin lutetium induces redox-sensitive apoptosis of vascular cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:759–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

