Novel anti-idiotype antibody therapy for lipooligosaccharide-induced experimental autoimmune neuritis: use relevant to Guillain-Barré syndrome
- PMID: 20077429
- PMCID: PMC3012786
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.22330
Novel anti-idiotype antibody therapy for lipooligosaccharide-induced experimental autoimmune neuritis: use relevant to Guillain-Barré syndrome
Abstract
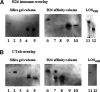
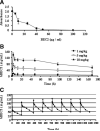
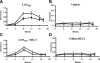
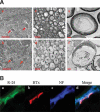
Campylobacteriosis is a frequent antecedent event in Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), inducing high-titer serum antibodies for ganglioside antigens in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Molecular mimicry between the lipooligosaccharide (LOS) component of Campylobacter jejuni and human peripheral nerve gangliosides is believed to play an important role in the pathogenesis of GBS. Conventional treatment strategies for patients with GBS include plasmapheresis, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and immunosuppression, which are invasive or relatively ineffective. In this study, we used our animal model of GBS, in which Lewis rats were immunized with GD3-like LOS isolated from C.jejuni. The animals developed anti-GD3 ganglioside antibodies and manifested neuromuscular dysfunction. To develop novel therapeutic strategies, we treated the animals by intraperitoneal administration of an anti-GD3 antiidiotype monoclonal antibody (BEC2) that specifically interacts with the pathogenic antibody. The treated animals had a remarkable reduction of anti-GD3 antibody titers and improvement of motor nerve functions. The results suggest that ganglioside mimics, such as antiidiotype antibodies, may be powerful reagents for therapeutic intervention in GBS by neutralizing specific pathogenic antiganglioside antibodies.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of a novel therapy for Lipo-oligosaccharide-induced experimental neuritis: use of peptide glycomimics.J Neurochem. 2010 Apr;113(2):351-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06627.x. Epub 2010 Feb 1. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20132479 Free PMC article.
-
The sialic acid residue is a crucial component of C. jejuni lipooligosaccharide ganglioside mimicry in the induction Guillain-Barré syndrome.J Neuroimmunol. 2006 May;174(1-2):126-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.02.009. Epub 2006 Mar 6. J Neuroimmunol. 2006. PMID: 16567003
-
Guillain-Barré syndrome-related Campylobacter jejuni in Bangladesh: ganglioside mimicry and cross-reactive antibodies.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43976. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043976. Epub 2012 Aug 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952833 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Campylobacter jejuni-induced Guillain-Barré syndrome from the Lewis rat model of experimental allergic neuritis.J Infect Dis. 1997 Dec;176 Suppl 2:S164-8. doi: 10.1086/513787. J Infect Dis. 1997. PMID: 9396704 Review.
-
Antiganglioside antibodies and their pathophysiological effects on Guillain-Barré syndrome and related disorders--a review.Glycobiology. 2009 Jul;19(7):676-92. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwp027. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Glycobiology. 2009. PMID: 19240270 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Axonal variants of Guillain-Barré syndrome: an update.J Neurol. 2021 Jul;268(7):2402-2419. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-09742-2. Epub 2020 Mar 5. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 32140865 Review.
-
The strategies used for treatment of experimental autoimmune neuritis (EAN): a beneficial effect of glatiramer acetate administered intraperitoneally.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012 Apr;42(2):181-8. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8246-7. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21234710
-
Biological Drugs in Guillain-Barré Syndrome: An Update.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(7):938-950. doi: 10.2174/1570159X14666161213114904. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27964705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified recombinant human IgG1-Fc is superior to natural intravenous immunoglobulin at inhibiting immune-mediated demyelination.Immunology. 2021 Sep;164(1):90-105. doi: 10.1111/imm.13341. Epub 2021 May 9. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33880776 Free PMC article.
-
The Promise of Anti-idiotype Revisited.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 12;10:808. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00808. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31031777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersen H, Nielsen JF, Nielsen VK. Inability of insulin to maintain normal nerve function during high-frequency stimulation in diabetic rat tail nerves. Muscle Nerve. 1994;17:80–84. - PubMed
-
- Ariga T, Yu RK. Antiglycolipid antibodies in Guillain-Barré syndrome and related diseases: review of clinical features and antibody specificities. J Neurosci Res. 2005;80:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Birren JE, Wall PD. Age changes in conduction velocity, refractory period, number of fibers, connective tissue space and blood vessels in sciatic nerve of rats. J Comp Neurol. 1956;104:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Buchwald B, Ahangari R, Weishaupt A, Toyka KV. Intravenous immunoglobulins neutralize blocking antibodies in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 2002;51:673–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

