Brain phenotypes in two FGFR2 mouse models for Apert syndrome
- PMID: 20077479
- PMCID: PMC2829947
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.22218
Brain phenotypes in two FGFR2 mouse models for Apert syndrome
Abstract
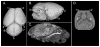
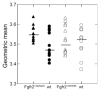
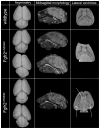
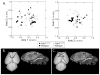
Apert syndrome (AS) is one of at least nine disorders considered members of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) -1, -2, and -3-related craniosynostosis syndromes. Nearly 100% of individuals diagnosed with AS carry one of two neighboring mutations on Fgfr2. The cranial phenotype associated with these two mutations includes coronal suture synostosis, either unilateral (unicoronal synostosis) or bilateral (bicoronal synostosis). Brain dysmorphology associated with AS is thought to be secondary to cranial vault or base alterations, but the variation in brain phenotypes within Apert syndrome is unexplained. Here, we present novel three-dimensional data on brain phenotypes of inbred mice at postnatal day 0 each carrying one of the two Fgfr2 mutations associated with AS. Our data suggest that the brain is primarily affected, rather than secondarily responding to skull dysmorphogenesis. Our hypothesis is that the skull and brain are both primarily affected in craniosynostosis and that shared phenogenetic developmental processes affect both tissues in craniosynostosis of Apert syndrome.
Copyright (c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Aldridge K, Kane A, Marsh J, Panchal J, Boyadijiev S, Yan P, Govier D, Ahmad W, Richtsmeier J. Brain morphology in nonsyndromic unicoronal craniosynostosis. Anat Rec. 2005;285:690–698. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Netherway D, Abbott A, Cox T, Roscioli T, David D. Analysis of intracranial volume in Apert syndrome genotypes. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2004;40:161–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

