The roles of apoptotic pathways in the low recovery rate after cryopreservation of dissociated human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 20077485
- PMCID: PMC3596802
- DOI: 10.1002/btpr.368
The roles of apoptotic pathways in the low recovery rate after cryopreservation of dissociated human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
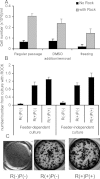
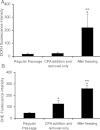
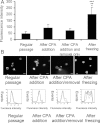
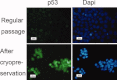
Human embryonic stem (hES) cells have enormous potential for clinical applications. However, one major challenge is to achieve high cell recovery rate after cryopreservation. Understanding how the conventional cryopreservation protocol fails to protect the cells is a prerequisite for developing efficient and successful cryopreservation methods for hES cell lines and banks. We investigated how the stimuli from cryopreservation result in apoptosis, which causes the low cell recovery rate after cryopreservation. The level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is significantly increased, F-actin content and distribution is altered, and caspase-8 and caspase-9 are activated after cryopreservation. p53 is also activated and translocated into nucleus. During cryopreservation apoptosis is induced by activation of both caspase-8 through the extrinsic pathway and caspase-9 through the intrinsic pathway. However, exactly how the extrinsic pathway is activated is still unclear and deserves further investigation.
Copyright 2010 American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Figures



References
-
- Gerecht-Nir S, Itskovitz-Eldor J. Human embryonic stem cells: a potential source for cellular therapy. Am J Transplant. 2004;4(Suppl 6):51–57. - PubMed
-
- Heng BC, Liu H, Toh WS, Rufaihah AJ, Yang Z, Bay BH, Ge Z, Quang HW, Lee EH, Cao T. Loss of viability during freeze-thaw of intact and adherent human embryonic stem cells with conventional slow-cooling protocols is predominantly due to apoptosis rather than cellular necrosis. J Biomed Sci. 2005;13:433–445. - PubMed
-
- Karlsson JOM, And Toner M. Cryopreservation. In: Lanza RP, Lang R, Vacanti J, editors. Pinciples of Tissue Engineering. San Diego: Academic Press; 2000. pp. 293–308.
-
- Salvesen GS. Caspase and apoptosis. Essays Biochem. 2002;38:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Nakano K, Vousden KH. PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 2001;7:683–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

