A postinfluenza model of Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia
- PMID: 20078212
- PMCID: PMC3664424
- DOI: 10.1086/650204
A postinfluenza model of Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Postinfluenza Staphylococcus aureus pneumonias are increasingly recognized as a major form of life-threatening infections.
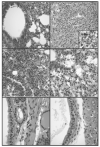
Methods: A mouse model of postinfluenza S. aureus pneumonia was developed. Mice were intranasally infected with bacteria alone or bacteria plus virus. Infection was assessed by mouse survival, lung histopathology, bacterial density in the lungs, and cellular response to infection.
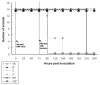
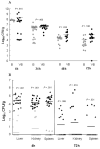
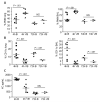
Results: Mice infected with both influenza virus and S. aureus showed higher mortality, greater lung parenchymal damage, and greater bacterial density at metastatic tissue sites than mice infected with only S. aureus. At 4 h, more polymorphonuclear leukocytes and fewer CD11c(+) cells were found in lung samples from mice infected with virus and bacteria than in those from mice infected with bacteria. alpha-Hemolysin and protein A were maximally expressed 4 h after infection, and Panton-Valentine leukocidin was maximally expressed 72 h after infection, with higher levels of alpha-hemolysin expression in mice infected with bacteria alone. Interferon gamma expression was higher in tissue collected from mice infected with virus plus bacteria than in those from bacteria-infected mice.
Conclusions: The results from this model demonstrate diverse effects caused by antecedent influenza virus infection, which have a profound influence on the morbidity and mortality associated with S. aureus pneumonia.
Figures
Comment in
-
Axis of coinfection evil.J Infect Dis. 2010 Feb 15;201(4):488-90. doi: 10.1086/650304. J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20078214 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin causes necrotizing pneumonia.Science. 2007 Feb 23;315(5815):1130-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1137165. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Science. 2007. PMID: 17234914
-
Community-acquired pneumonia due to Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in an HIV-2-infected patient.Int J STD AIDS. 2011 Oct;22(10):610-2. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2009.009372. Int J STD AIDS. 2011. PMID: 21998186
-
Necrotizing pneumonia with Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes: an underestimated gravity?Eur J Intern Med. 2012 Jul;23(5):e128-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2012.04.003. Epub 2012 Apr 29. Eur J Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 22726383 No abstract available.
-
Pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus necrotizing pneumonia: the role of PVL and an influenza coinfection.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013 Oct;11(10):1041-51. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2013.827891. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013. PMID: 24073746 Review.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)-associated staphylococcal pneumonia.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007 Oct;30(4):289-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.04.019. Epub 2007 Jul 12. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007. PMID: 17629464 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-influenza pneumonia caused by the USA300 community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2012 Mar;27(3):313-6. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.3.313. Epub 2012 Feb 23. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22379344 Free PMC article.
-
Pyopericarditis and tropical pyomyositis: unusual concomitance.Autops Case Rep. 2012 Mar 30;2(1):49-53. doi: 10.4322/acr.2012.008. eCollection 2012 Jan-Mar. Autops Case Rep. 2012. PMID: 31528562 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal H3N2 influenza A virus fails to enhance Staphylococcus aureus co-infection in a non-human primate respiratory tract infection model.Virulence. 2013 Nov 15;4(8):707-15. doi: 10.4161/viru.26572. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Virulence. 2013. PMID: 24104465 Free PMC article.
-
Time and dose-dependent risk of pneumococcal pneumonia following influenza: a model for within-host interaction between influenza and Streptococcus pneumoniae.J R Soc Interface. 2013 Jul 3;10(86):20130233. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2013.0233. Print 2013 Sep 6. J R Soc Interface. 2013. PMID: 23825111 Free PMC article.
-
Linezolid and Its Immunomodulatory Effect: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 28;10:1389. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01389. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31849655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Herold BC, Immergluck LC, Maranan MC, et al. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children with no identified predisposing risk. JAMA. 1998;279:593–598. - PubMed
-
- Grundmann H, Aires-de-Sousa M, Boyce J, Tiemersma E. Emergence and resurgence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a public-health threat. Lancet. 2006;368:874–885. - PubMed
-
- Lina G, Piemont Y, Godail-Gamot F, et al. Involvement of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in primary skin infections and pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:1128–1132. - PubMed
-
- Francis JS, Doherty MC, Lopatin U, et al. Severe community-onset pneumonia in healthy adults caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying the Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:100–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

