The impact of SLCO1B1 polymorphisms on the plasma concentration of lopinavir and ritonavir in HIV-infected men
- PMID: 20078617
- PMCID: PMC2830602
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03551.x
The impact of SLCO1B1 polymorphisms on the plasma concentration of lopinavir and ritonavir in HIV-infected men
Abstract
What is already known about this subject: * There is large interindividual variability in the pharmacokinetics of protease inhibitors (PIs) among human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals under highly active antiretroviral therapy. * Protease inhibitor have been recently reported to be substrates of the SLCO1B1/OATP1 drug transporter. * A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the SLCO1B1 gene (521T-->C) was associated with plasma levels of lopinavir in HIV-infected individuals.
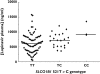
What this study adds: * Data on the impact of three SLCO1B1 SNPs (521T-->C, 388A-->G, 463C-->A) on the trough plasma concentration of lopinavir and ritonavir in a cohort of 99 adult HIV-infected Brazilian men under stable highly active antiretroviral therapy. * Evidence that carriers of the 521C allele display significantly higher lopinavir, but not ritonavir plasma concentrations relative to the wild-type TT genotype. * No effect of either 388A-->G or 463C-->A SNPs on lopinavir or ritonavir plasma concentrations. * Further studies are required to confirm the clinical significance of the association between the SLCO1B1521T-->C polymorphism and lopinavir pharmacokinetics.
Aims: To investigate possible associations between three SLCO1B1 single nucleotide polymorphisms (388A-->G, 463C-->A, 521T-->C) and lopinavir/ritonavir plasma concentrations.
Methods: The study included 99 human immunodeficiency virus-infected men on stable highly active antiretroviral therapy containing lopinavir/ritonavir. Trough concentrations of lopinavir and ritonavir in plasma were quantified using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Genotyping of SLCO1B1388A-->G, 463C-->A and 521T-->C polymorphisms was performed by allelic discrimination using real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results: The trough concentration of lopinavir in plasma is significantly associated with SLCO1B1521T-->C genotypes (P= 0.03). There is a significant trend for increasing concentrations of lopinavir from TT to TC to CC genotypes (P= 0.02). Carriers of the 521C allele display significantly higher lopinavir plasma concentrations relative to the wild-type TT genotype (P= 0.03).
Conclusions: Reduced uptake of lopinavir by hepatocytes in carriers of the 521C allele may account for these results, but further studies to confirm the clinical importance of SLCO1B1 polymorphisms in lopinavir pharmacokinetics are warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ABCB1 polymorphisms and the concentrations of lopinavir and ritonavir in blood, semen and saliva of HIV-infected men under antiretroviral therapy.Pharmacogenomics. 2009 Feb;10(2):311-8. doi: 10.2217/14622416.10.2.311. Pharmacogenomics. 2009. PMID: 19207033
-
CYP3A5, ABCB1, and SLCO1B1 polymorphisms and pharmacokinetics and virologic outcome of lopinavir/ritonavir in HIV-infected children.Ther Drug Monit. 2011 Aug;33(4):417-24. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0b013e318225384f. Ther Drug Monit. 2011. PMID: 21743379 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of the effect of SLCO1B1 polymorphisms on lopinavir plasma concentration in HIV-infected adults.Antivir Ther. 2012;17(5):861-8. doi: 10.3851/IMP2095. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Antivir Ther. 2012. PMID: 22477766 Free PMC article.
-
SLCO1B1 polymorphism and oral antidiabetic drugs.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010 Oct;107(4):775-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00581.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20406215 Review.
-
Safety and antiviral activity of lopinavir/ritonavir-based therapy in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Aug;56(2):273-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki209. Epub 2005 Jun 30. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15994247 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacogenetics in the brazilian population.Front Pharmacol. 2010 Oct 4;1:118. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2010.00118. eCollection 2010. Front Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 21833165 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacogenetics study of the antituberculosis drug PA-824 with concomitant lopinavir-ritonavir, efavirenz, or rifampin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Sep;58(9):5245-52. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03332-14. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24957823 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Frequency of functional exonic single-nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotype distribution in the SLCO1B1 gene across genetic ancestry groups in the Qatari population.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 1;12(1):14858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19318-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36050458 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of SLCO1B1 polymorphisms on lopinavir Ctrough in Serbian HIV/AIDS patients.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;86(7):1289-1295. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14230. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32022294 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of the SLCO1B1 388A>G and the 521T>C polymorphism in Tanzania genotyped by a new LightCycler®-based method.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;67(11):1139-45. doi: 10.1007/s00228-011-1065-9. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21630030
References
-
- Owen A, Pirmohamed M, Khoo SH, Back DJ. Pharmacogenetics of HIV therapy. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2006;16:693–703. - PubMed
-
- Mahungu TW, Johnson MA, Owen A, Back DJ. The impact of pharmacogenetics on HIV therapy. Int J STD AIDS. 2009;20:145–51. - PubMed
-
- Leschziner GD, Andrew T, Pirmohamed M, Johnson MR. ABCB1 genotype and PGP expression, function and therapeutic drug response: a critical review and recommendations for future research. Pharmacogenomics J. 2007;7:154–79. - PubMed
-
- Estrela RC, Santoro AB, Barroso PF, Tuyama M, Suarez-Kurtz G. CYP3A5 genotype has no impact on plasma trough concentrations of lopinavir and ritonavir in HIV-infected subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008;4:205–7. - PubMed
-
- Josephson F, Allqvist A, Janabi M, Sayi J, Aklillu E, Jande M, Mahindi M, Burhenne J, Bottiger Y, Gustafsson LL, Haefeli WE, Bertilsson L. CYP3A5 genotype has an impact on the metabolism of the HIV protease inhibitor saquinavir. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;81:708–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases